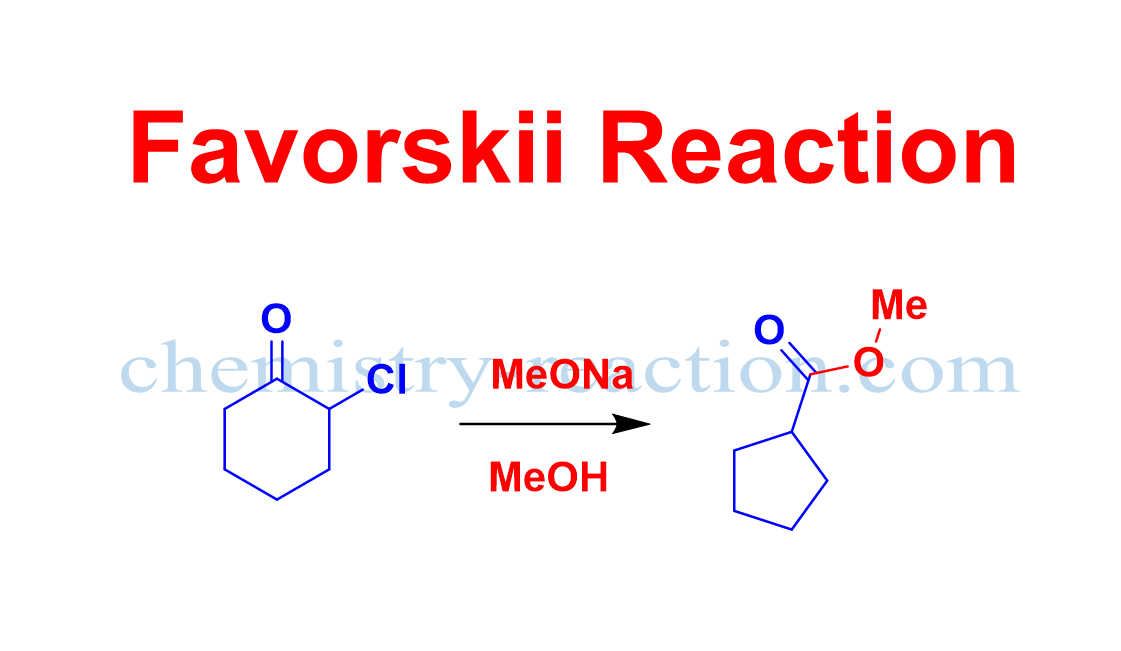
Favorskii Rearrangement
What is Favorskii Rearrangement explain? Favorskii Rearrangement is organic reaction of α-halo ketones (chlorine, bromine, or iodine) having at least one α-hydrogen, with a nucleophile (alcohol, amine, or H2O) in the presence base (usually an alkoxide or hydroxide) give carboxylic acids or carboxylic acid derivatives via a cyclopropanone intermediate. It is widely used organic reaction … Read more