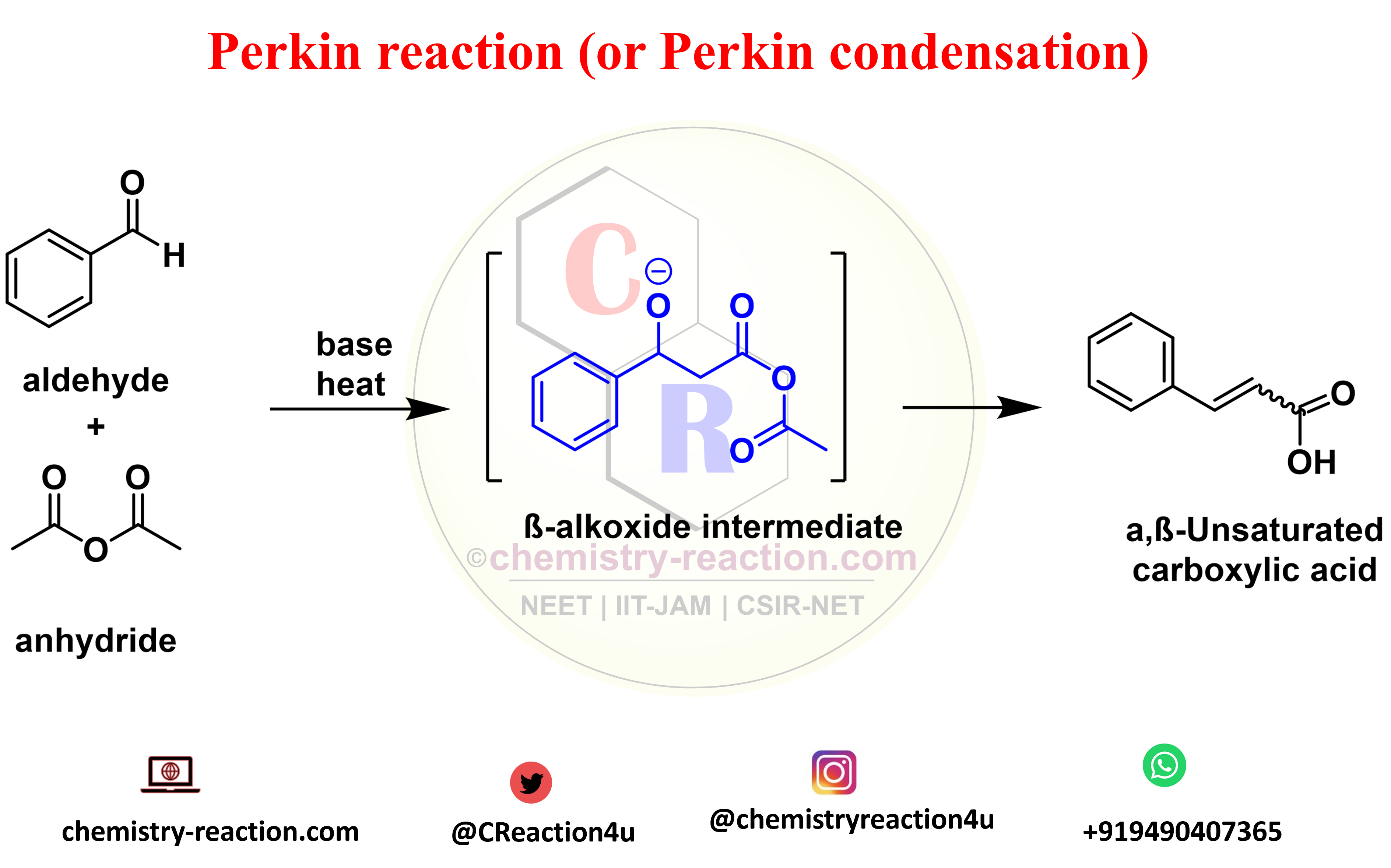
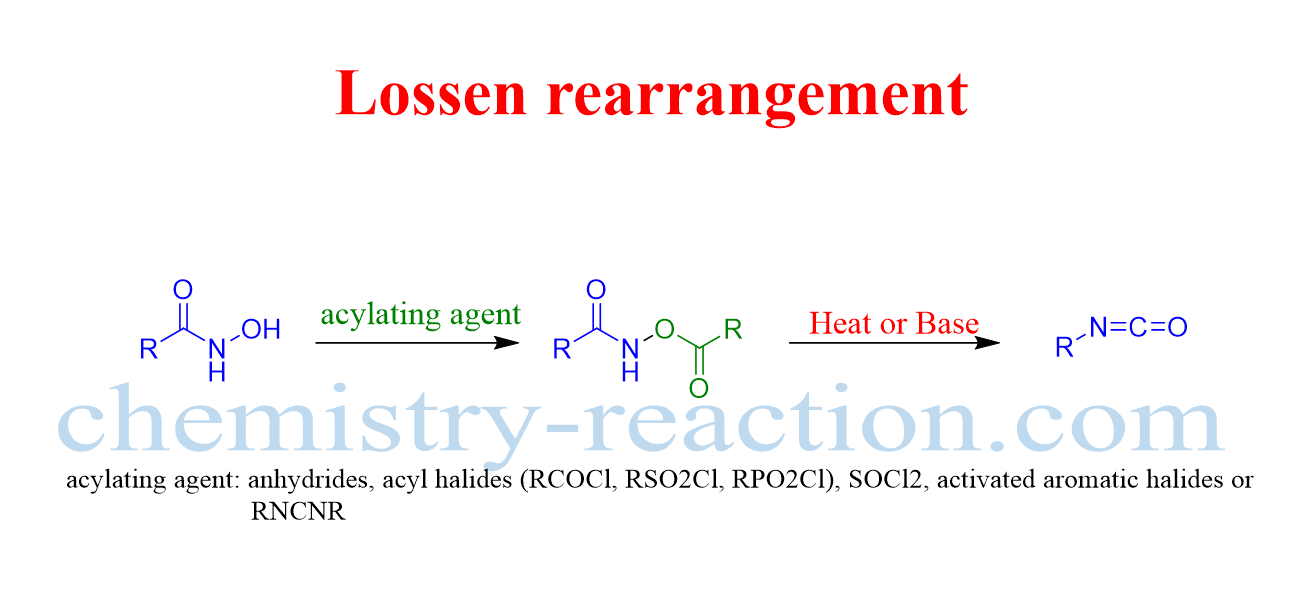
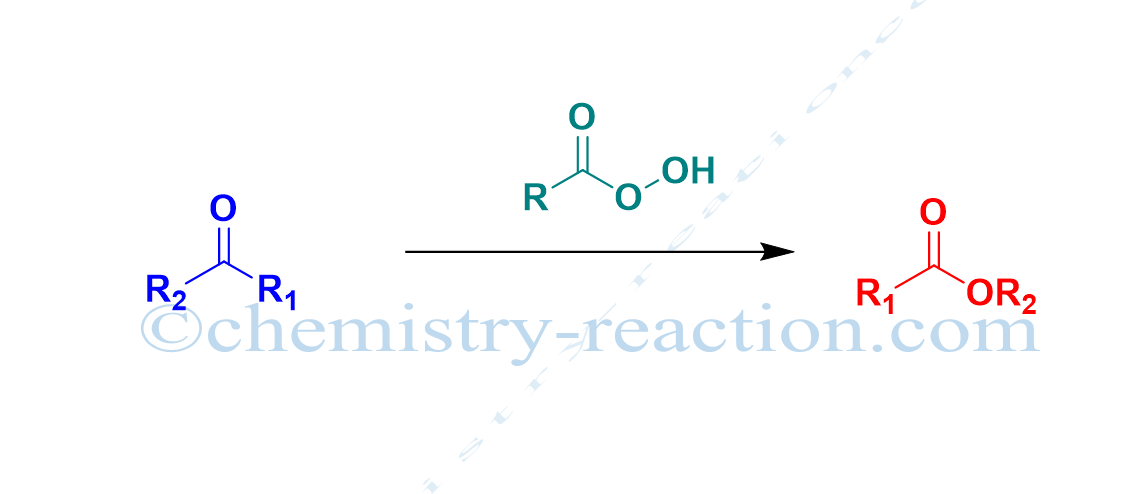
Schmidt Reaction (Rearrangement): definition| Mechanism| example
Schmidt reaction is a acid-catalyzed Rearrangement reaction of hydrazoic acid reactions of electrophiles, like carbonyl compounds, alkenes tertiary and alcohols. The following these substrates include amines, nitriles, amides or imines, rearrangement and extrusion of nitrogen.