Baker-Venkataraman Rearrangement is the base-promoted (KOH) rearrangement of aromatic 2-acyloxy ketones to the corresponding aromatic 1,3-diketone (β-diketones); it is a well-known synthetic intermediate in organic chemistry, the reaction and also known as Baker-Venkataraman synthesis. here is the Mechanism of Baker-Venkataraman Rearrangement with Application , Examples and Use.
The commonly used bases are potassium tert-butoxide, Na in methylbenzene, NaH or KH, pyridine, and PPh3Na. This reaction is similar to the Claisen Condensation because both reactions proceed through the formation of an enolate after intramolecular acyl transfer. (baker-venkataraman synthesis of flavones)
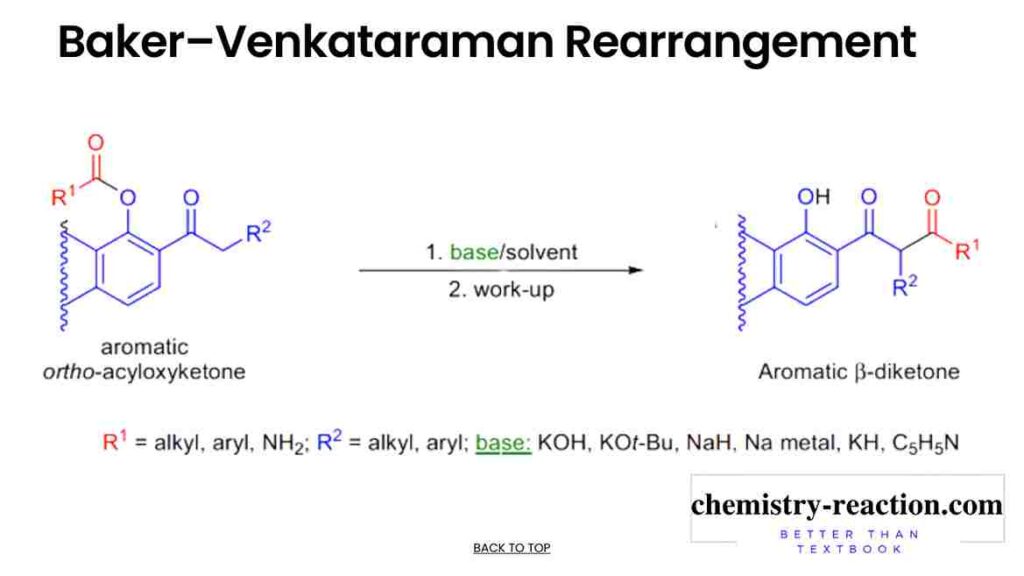
Table of Page Contents
Mechanism:
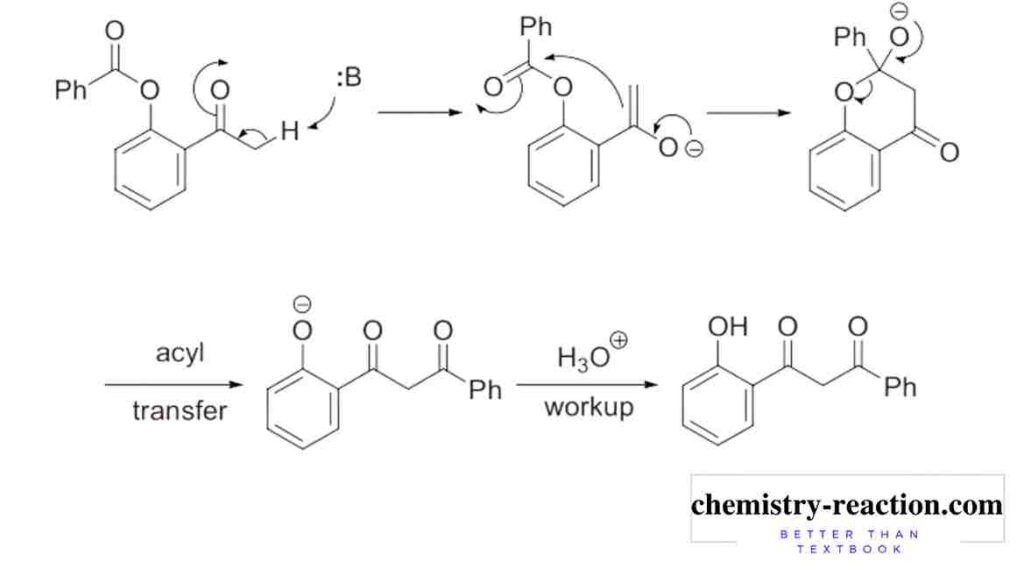
Mechanism of Baker-Venkataraman Rearrangement firs step the ketone is deprotonated at the α-carbon and an enolate is generated. This enolate nucleophile will attacks on the carbonyl carbon of the acyloxy moiety, (this is intramolecular reaction). and tetrahedral intermediate will form that subsequently breaks down to form the aromatic 1,3-diketone (β-diketones).
Application :
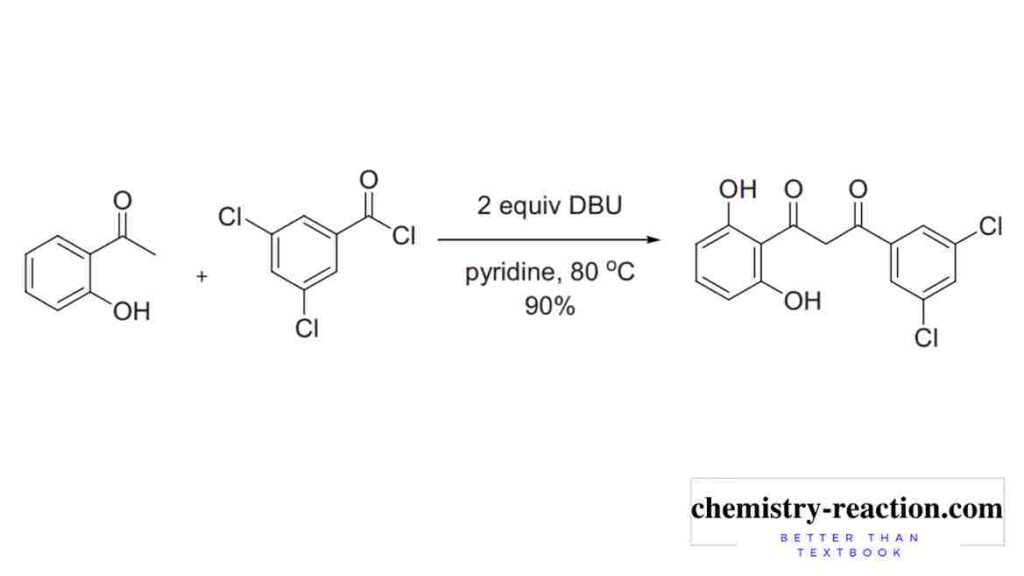
Baker−Venkataraman Rearrangement Application is preparation of 1,3-diketone, ester substrate. 1,3-diketone (β-diketones) play important role in chromones, flavones, isoflavones, and coumarins synthesis.
Use :
Baker–Venkataraman Rearrangement Used for total synthesis of aklanonic acid and its derivatives.
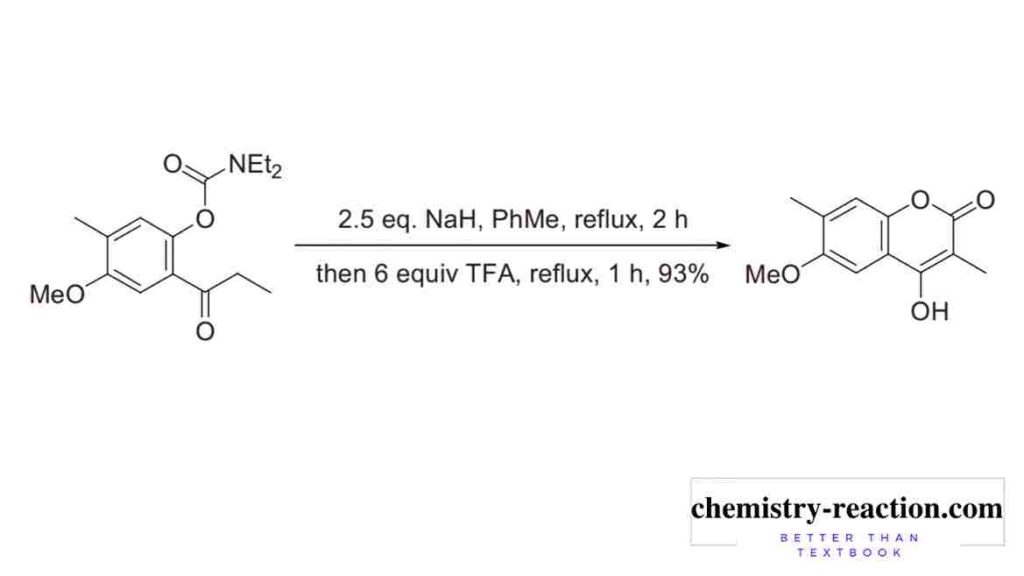
Examples:
Baker–Venkataraman Synthesis Examples
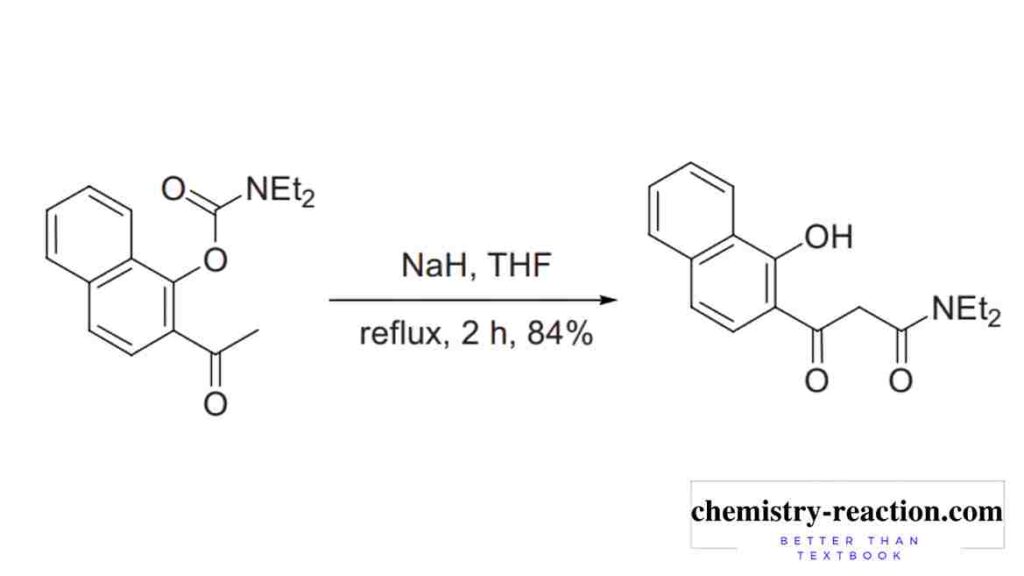
baker-venkataraman synthesis of flavones
Allan–Robinson reaction
Kostanecki acylation
Related Reaction :
- Claisen Condensation
- Stetter Reaction
- Wacker Oxidation
- Stork Enamine Synthesis
References:
- Microwave-assisted synthesis and antimicrobial activities of flavonoid derivatives-sciencedirect
- Molecular rearrangement of some o-acyloxyacetophenones and the mechanism of the production of 3-acylchromones –Journal of the Chemical Society
- Org. Synth. 1952, 32, 72 DOI: 10.15227/orgsyn.032.0072
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.
1 thought on “Baker-Venkataraman Rearrangement”