Table of Page Contents
What is Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation (Baeyer-Villeger Reaction) explain?
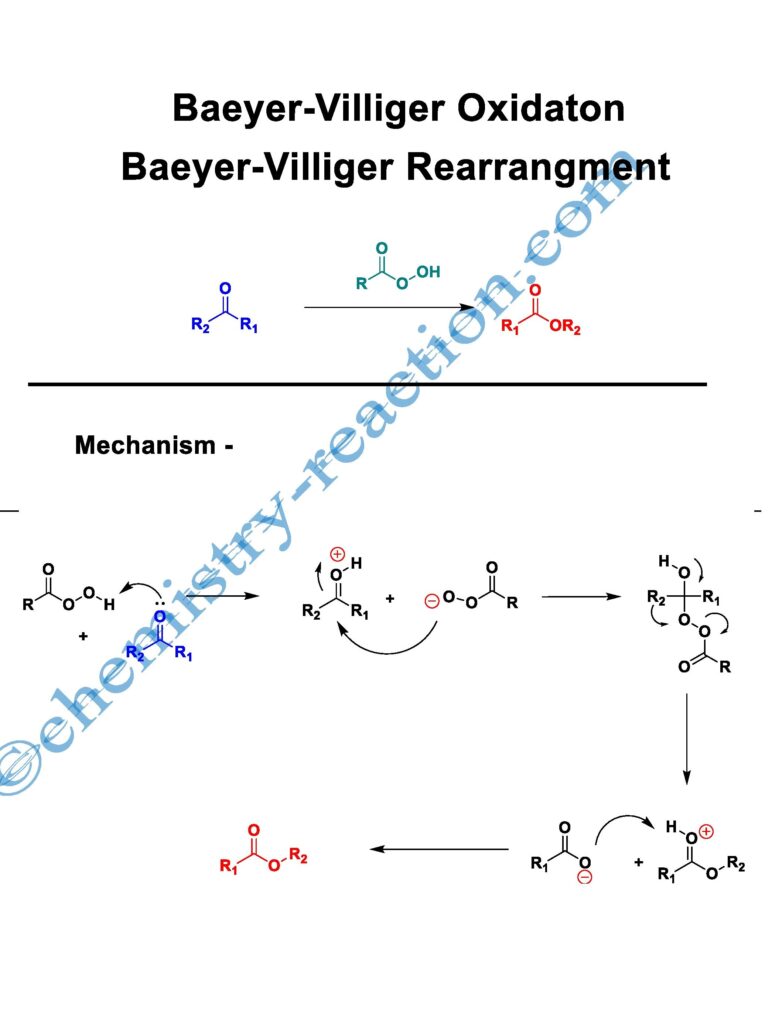
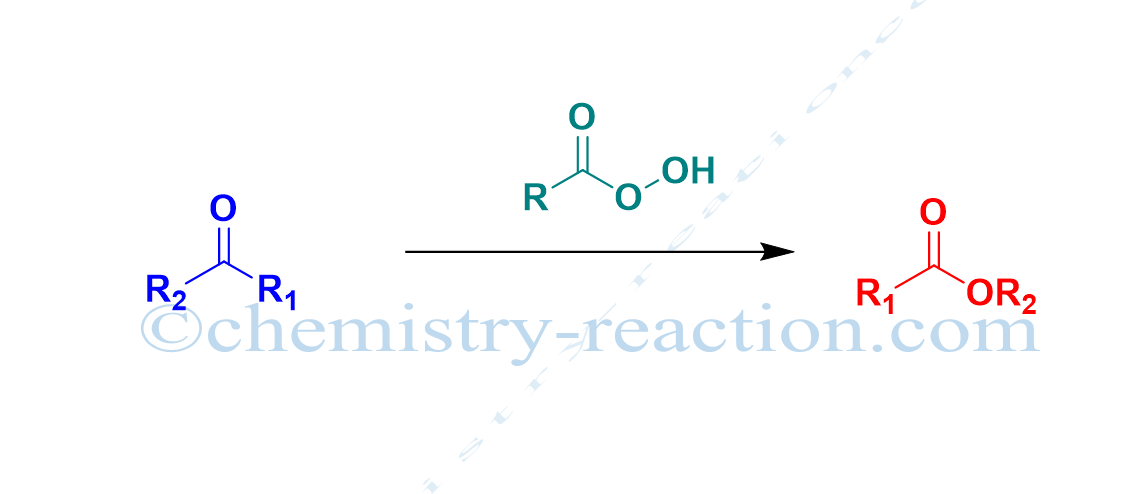
Baeyer-Villiger oxidation (Baeyer-Villeger Reaction) is the conversion of ketone (cyclic ketone, aromatic ketone, aliphatic ketone) into corresponding esters (lactones) by using MCBPA, or hydrogen peroxide as oxidant and a Lewis acid is known as Baeyer-Villiger oxidation (Baeyer-Villeger Reaction).
A. Baeyer and V. Villiger discovered the reaction. Baeyer-Villiger oxidation is also called the Baeyer-Villeger Rearrangement Reaction.

Baeyer-Villiger Rearrangement Mechanism :
In the first step of Baeyer-Villiger oxidation mechanism, the peroxy acid protonates the carbonyl group. It increases the electrophilicity of ketone, and then the peroxy acid anion adds to this cationic species to form the intermediate (Criegee).
In the next step, immediately alkyl group will migrate on electron-deficient oxygen, and simultaneously carboxylic acid departs from this intermediate. This process is assumed as a concerted process.
The rearrangement occurs with retention of the stereochemistry at the migrating core.
The migratory aptitude of alkyl groups in Baeyer-Villiger Rearrangement-
Baeyer villiger oxidation migratory aptitude R = tertiary alkyl > secondary alkyl > aryl > primary alkyl > methyl,
Baeyer-Villiger oxidation peracids reactivity-
CF3CO3H > monopermaleic acid > monoperphthalic acid > 3,5-dinitroperbenzoic acid > p-nitroperbenzoic acid > mCPBA ~ performic acid > perbenzoic acid > peracetic acid » H2O2 > t-BuOOH.

Application of Baeyer–Villiger Oxidation Reaction:
Synthesis of 3-hydroxyindole-2-carboxylates.
Related Reactions:
Reference:
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.
3 thoughts on “Baeyer-Villiger Rearrangement (Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation):”