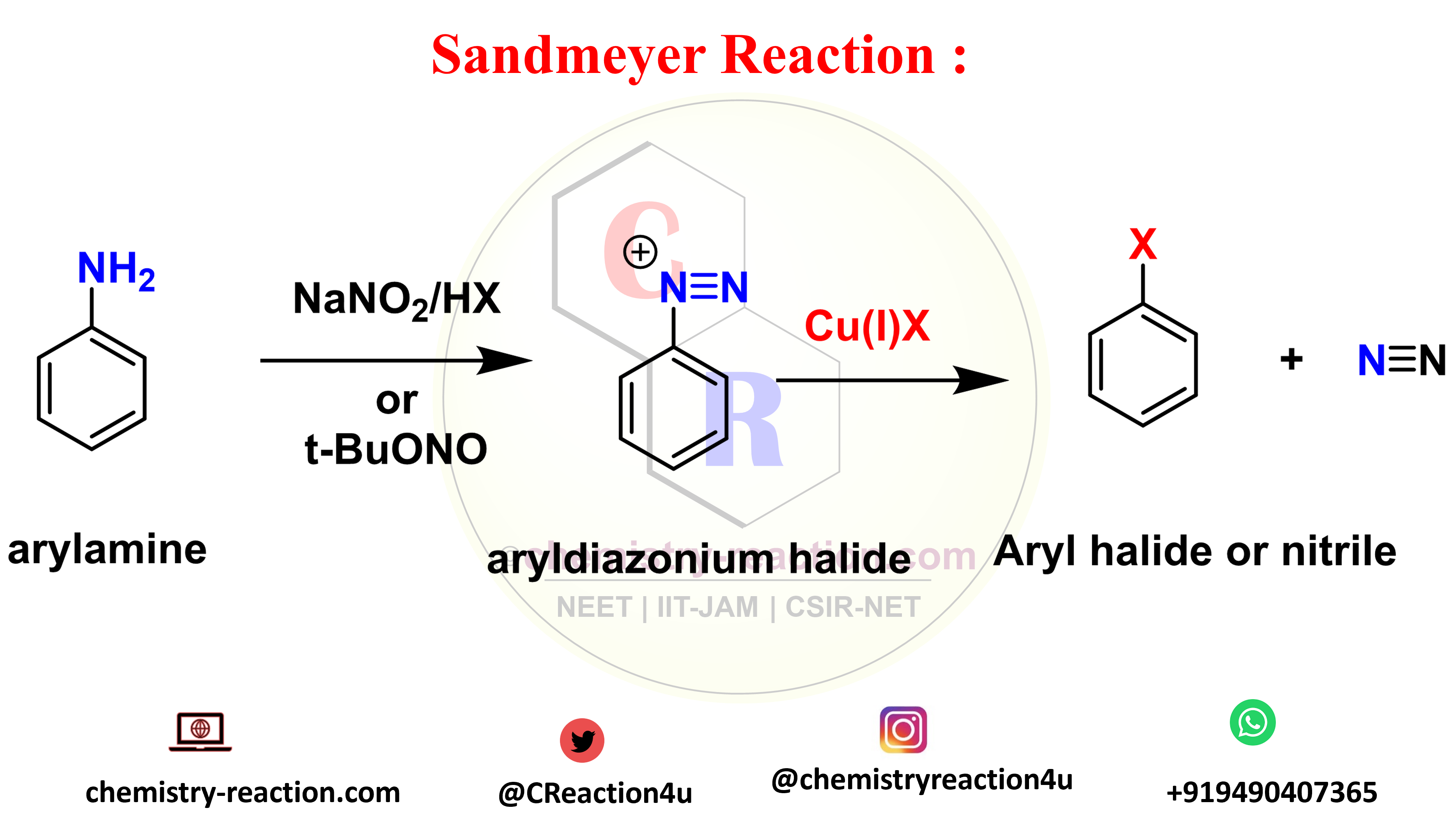
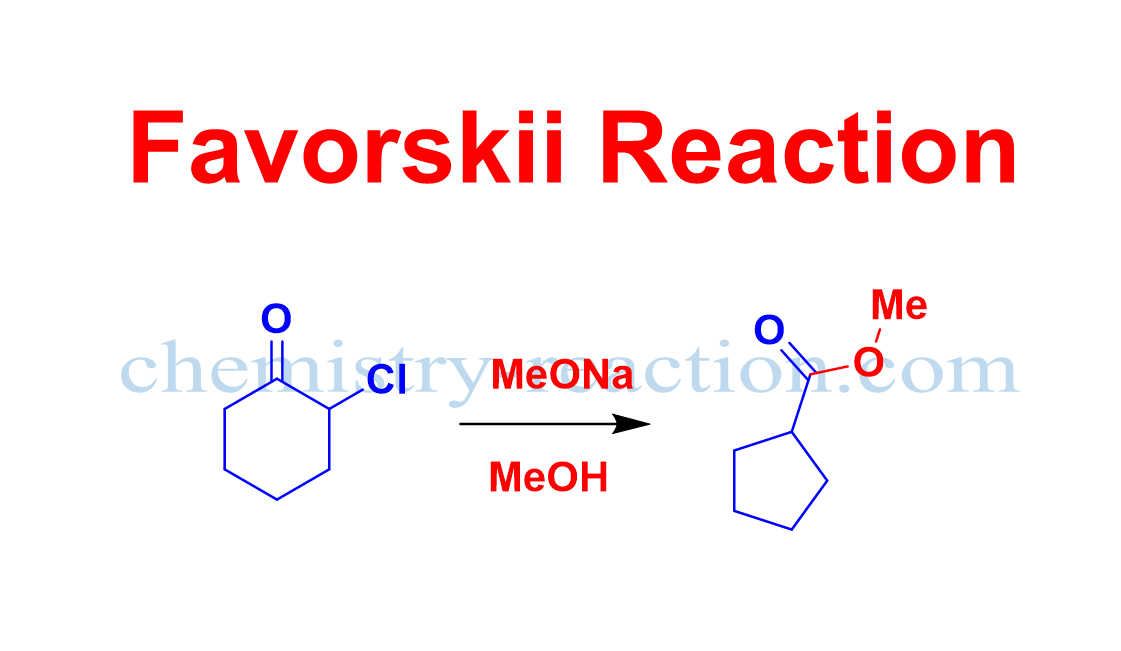
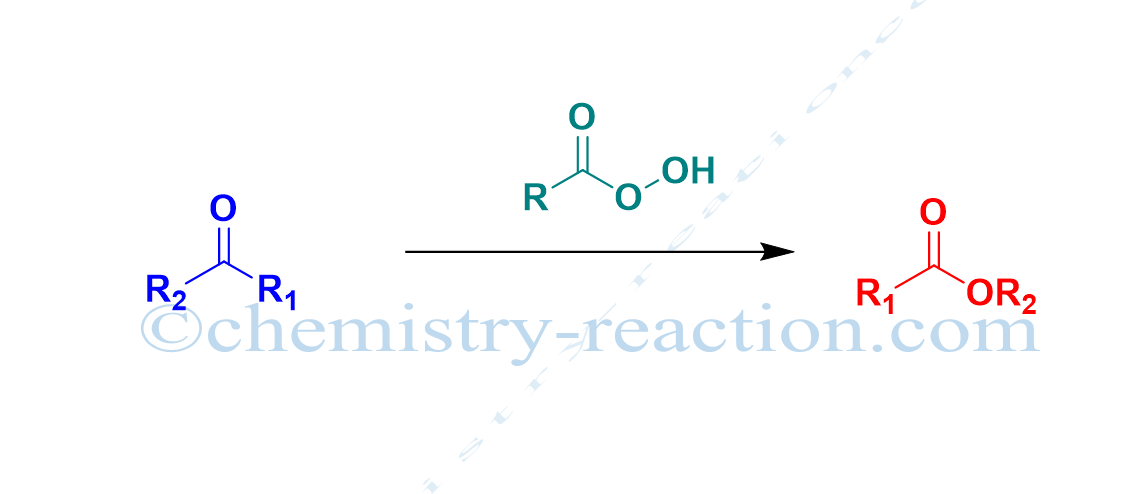
Sandmeyer Reaction: Definition| Mechanism| Example| Application
The Sandmeyer reaction is an organic substitution type reaction used for the synthesis of aryl halide from an aryl diazonium salt. the catalyst used in Sandmeyer reaction is a copper(I) halide like chloride, bromide or iodide ions catalyst. significantly, The reaction include trifluoromethylation, hydroxylation, cyanation, and halogenation type reaction on benzene.