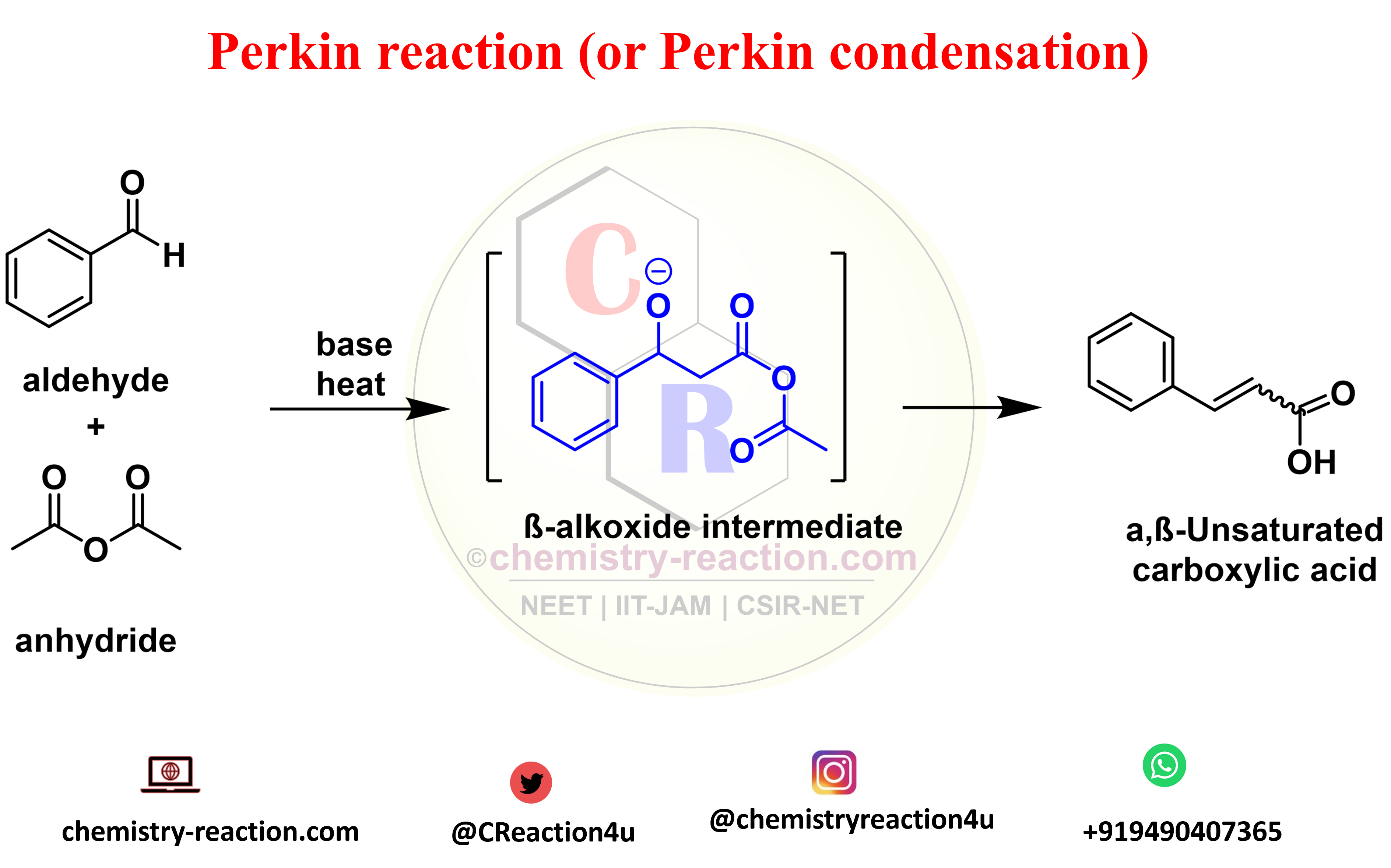
Perkin Reaction (Perkin Condensation): definition| mechanism| example| application
The Perkin reaction (or Perkin condensation) is an condensation of aromatic aldehydes and the anhydrides of aliphatic carboxylic acids in the presence of a weak base to obtain α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acids