Table of Page Contents
What is Polonovski reaction?
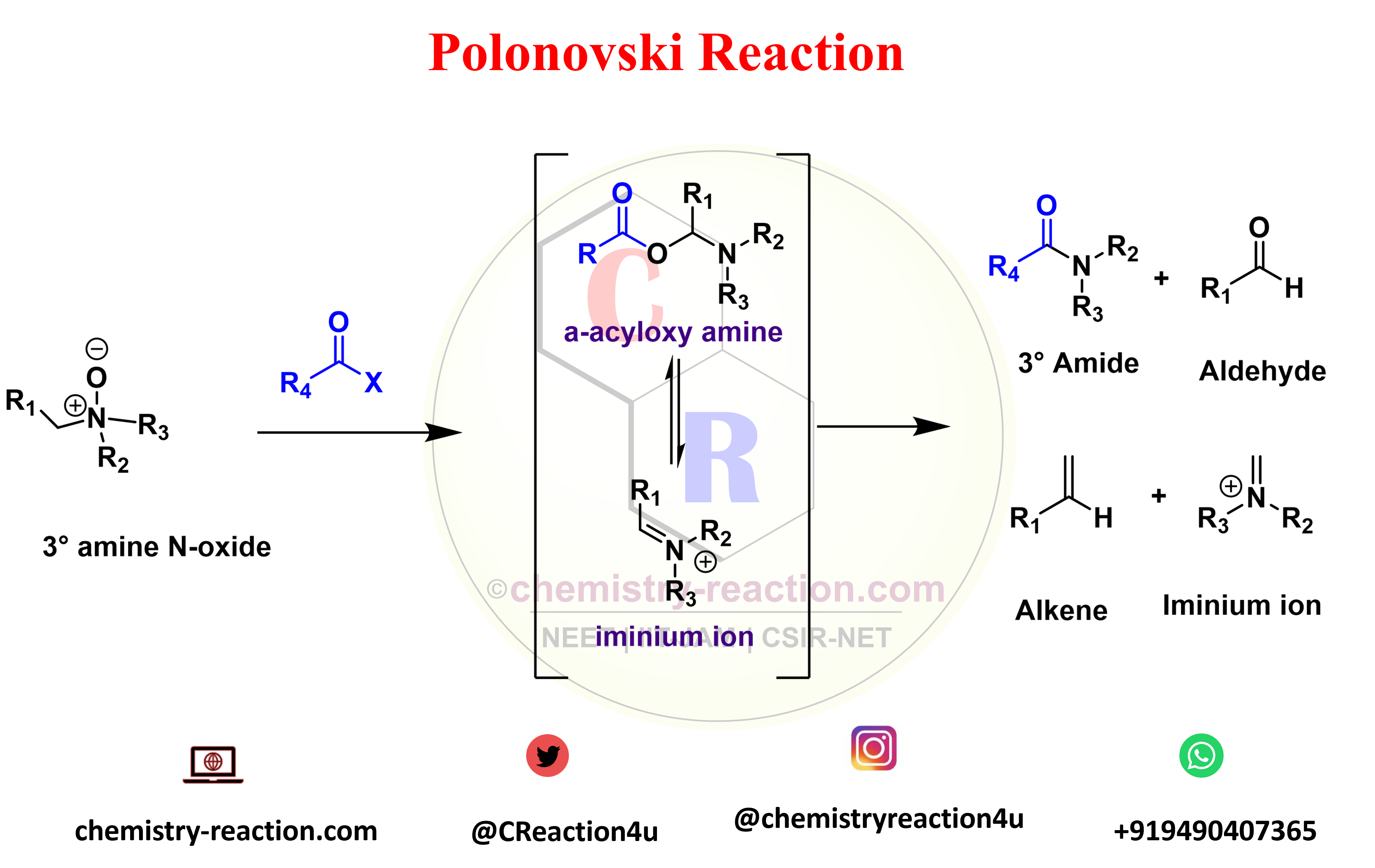
Polonovski reaction is organic rearrangement type reaction used for the N-demethylation of tert-amines. The activation of tertiary amine N-oxides with anhydrides or acyl halides to prepare the corresponding intermediates (iminium ion). Polonovski Reaction known as n-oxide rearrangement.
Polonovski reported that the alkaloid N-oxides treatment with acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride underwent a rearrangement (polonovski rearrangement) in which one of the alkyl groups linked to the nitrogen was cleaved (pyrolysis of amine oxides) the N-acetyl derivative of the alkaloid was obtained.
R1 = H, alkyl, aryl, heteroaryl; R2-3 = CH3, alkyl, aryl; R4 = CH3, CF3 (Polonovski-Potier rxn); X = Cl, Br, OCOR4, BF4 – , ClO4 – , SbF6 –
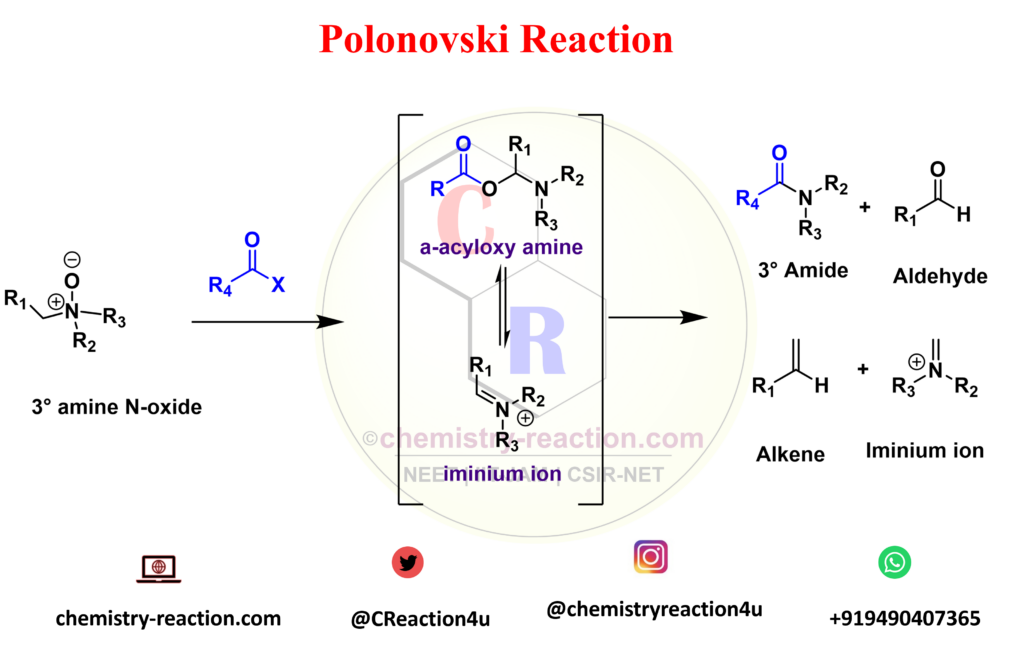
Polonovski Reaction Mechanism :
The conversion of the O-acylimonium salt to the imine proceeds via an E2-type elimination. The hydrogen that is
antiperiplanar to the N-O bond is usually removed preferentially. When the N-oxide is activated with iron salts, a SET mechanism is operational, while with SO2 an intramolecular ionic mechanism is most likely.

Related reactions:
- Beckmann Rearrangement
- Benzilic Acid Rearrangement
- Brook Rearrangement
- Favorskii Rearrangement
- Lossen Rearrangement
- Prins-Pinacol Rearrangement
- Pummerer Rearrangement
Reference:
- Ferris, J. P. etal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 5270-5275.
- Ziegler,etal J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 1083-1094.
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.
3 thoughts on “Polonovski Reaction”