Table of Page Contents
What is Pomeranz-Fritsch Reaction?
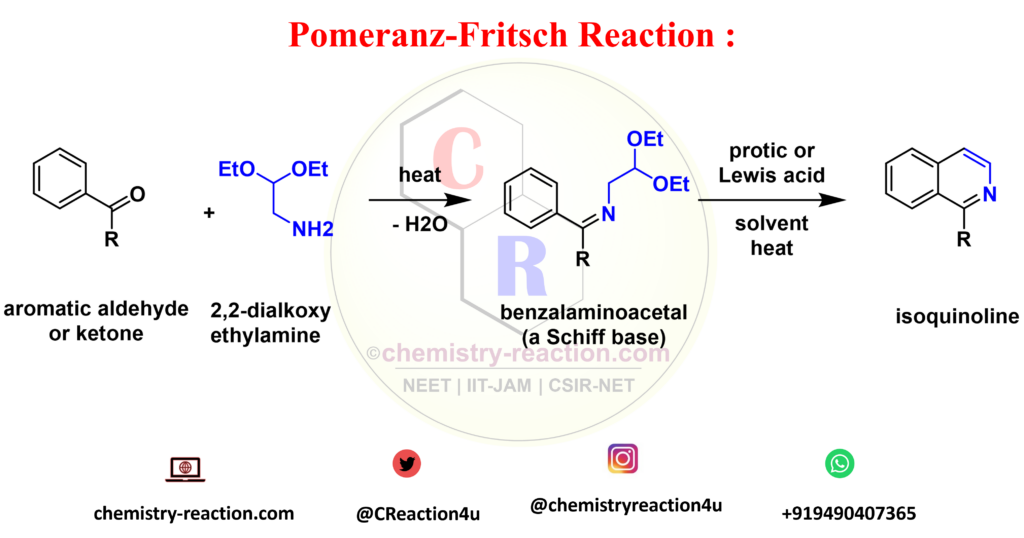
Pomeranz-Fritsch Reaction is acid-catalyzed Synthesis of isoquinoline by heatingcyclization of benzalaminoacetals (these are Schiff bases) to give substituted isoquinolines is known as the Pomeranz-Fritsch reaction.
The benzalaminoacetals are prepared by reacting 2,2-dialkoxyethylamines with substituted aromatic aldehydes or rarely with aromatic ketones.
starting materials reactant used in pomeranz-fritsch synthesis of isoquinoline are benzalaminoacetals and aromatic ketones. pomeranz-fritsch synthesis of isoquinoline in pomeranz fritsch reaction intermediate is benzalaminoacetal (a Schiff base).
R = usually an electron-donating group (EDG), H, alkyl, aryl, O-alkyl, Cl, Br; protic acid: H2SO4, HCl, PPA; Lewis acid: BF3·OEt2
Pomeranz-Fritsch Reaction Mechanism:
In Pomeranz-Fritsch Reaction Mechanism the First step is the benzalaminoacetal a (Schiff base) is formed by the condensation of benzaldehyde and a 2,2-dialkoxyethylamine. next step the condensation a hydrogen is added to one of the alkoxy groups. Subsequently, an -OEt is removed. Next, the aromatic ring will attack on cation and form c-c bond. After that a second hydrogen-atom is added to the compound. In the last step a second -OEt is removed and the bicyclic system becomes aromatic system.

Related reactions:
Reference:
- Pomeranz, C. (December 1893). “Uber eine neue Isochinolinsynthese”. Monatshefte für Chemie. 14 (1): 116–119.
- Kürti, László; Czakó, Barbara (2007). Strategic applications of named reactions in organic synthesis : background and detailed mechanisms ; 250 named reactions (Pbk. ed., [Nachdr.]. ed.). Amsterdam [u.a.]: Elsevier Academic Press. pp. 358–359.
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.