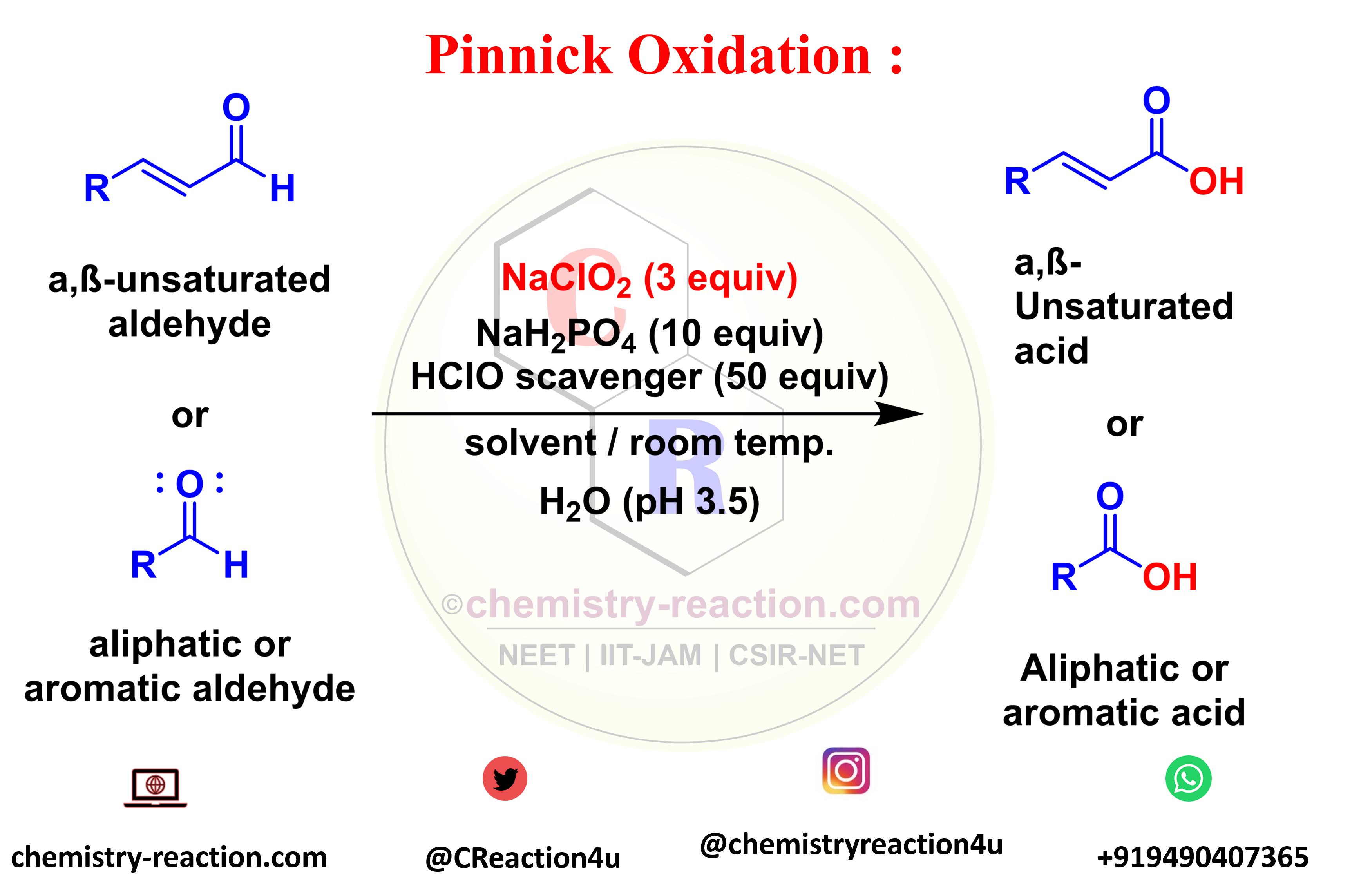
What does Pinnick oxidation ?
Pinnick oxidation does Selective oxidation of Aldehydes to carboxylic acids.
The transformation of aldehydes (aliphatic, aromatic, saturated, or unsaturated) to the corresponding carboxylic acids is known as the Pinnick Oxidation. The Pinnick oxidation procedure is the NaClO2/2-methyl-2-butene the system was generally used to oxidize a wide range of α and β-unsaturated Aldehydes without affecting any of the double bonds present in the substrate.
pinnick oxidation reagents : NaClO2 (1-3 equiv) or R2 H O, NaH2PO4 (7-10 equiv) H2O (pH 3.5).
R = H, alkyl, aryl, alkenyl, allyl, homoallyl; scavenger = 2-methyl-2-butene, H2O2,
H2NSO3H, m-C6H4(OH)2, DMSO; solvent = t-BuOH, t-BuOH/THF
Pinnick oxidation mechanism :
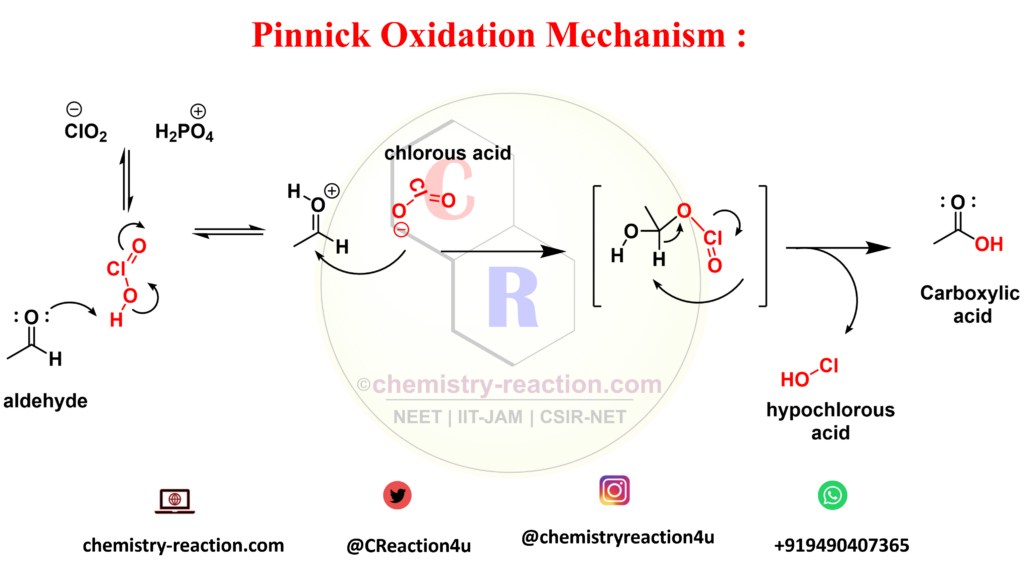
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.
1 thought on “Pinnick oxidation”