This reaction is also known as Hunsdiecker–Borodin reaction or Borodin reaction in organic chemistry. Hunsdiecker reaction is a chemical reaction involved functional group interconversion of a carboxylic acid (benzoic acid) into an alkyl halide, usually a bromide or iodide, involving the loss of one carbon atom, which is eliminated as CO2. chemical equation has shown above.
hunsdiecker reaction is given by German husband-and-wife team of Heinz and Cläre Hunsdiecker in 1942. hunsdiecker reaction is a chemical reaction used for the preparation of alkyl halide. hunsdiecker reaction reagent are halides, and silver oxide.
Table of Page Contents
Mechanism:
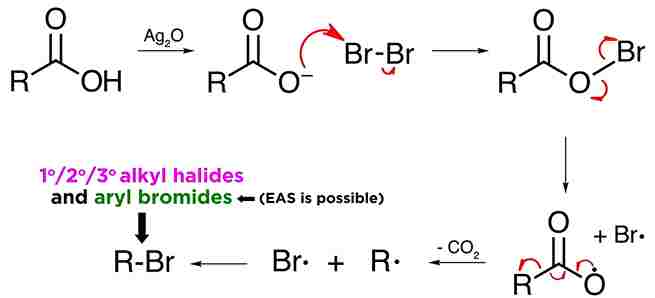
Hunsdiecker reaction mechanism involve free radicals. First of all, the silver carboxylate must be made, which can be prepared by mixing the carboxylic acid with silver oxide. Removal of water leads to the isolation of the silver salt.
Silver carboxylates react with halogens like bromine to form acyl hypohalites, in this case the acyl hypobromite. The driving force for the reaction is provided by the formation of silver bromide, AgBr, which is highly insoluble and precipitates. Now, given that oxygen-bromine bonds are quite weak, these acyl hypobromites tend to break.
oxygen and bromine are highly electronegative, and neither atom wants to give up a pair of electrons, they split the pair evenly, and therefore both radicals will generate. Carboxylate radicals slowly decarboxylate in the following manner, thereby producing an alkyl radical. form the alkyl halide.
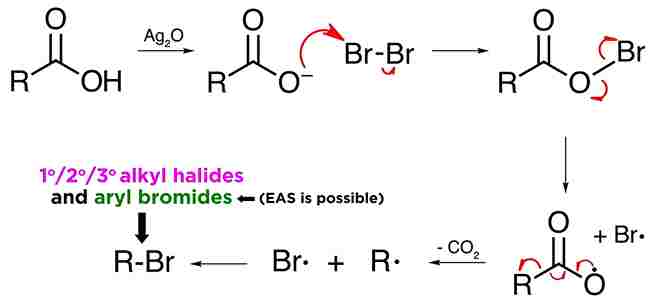
The reaction can produce primary, secondary, or tertiary alkyl halides, and also aryl bromides, via this mechanism.
Side reaction:
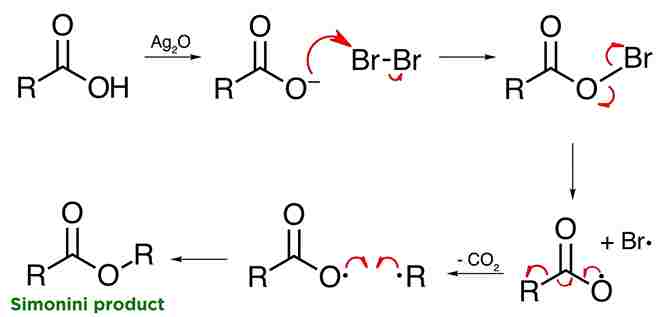
Hunsdiecker Reaction, Side reaction is electrophilic bromination of the benzene ring, especially if the aromatic ring is very electron rich referred to as the Simonini reaction.
Application and Modification:
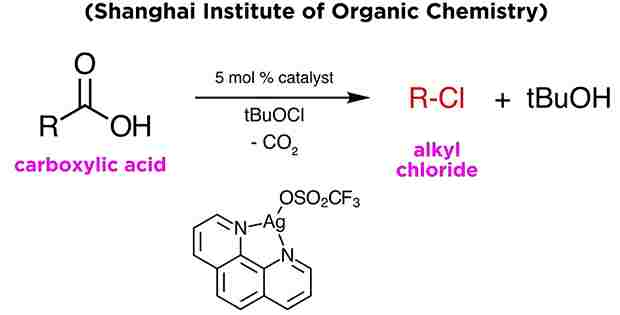
- Hunsdiecker Reaction have been many modifications of this decarboxylative bromination. Some methods application even more toxic salts than silver, like mercury or lead carboxylates. These alternatives are even less practical than the original Hunsdiecker protocol.
- As an example, let’s highlight the work of Professor Chaozhong Li, from the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry
Related Reaction:
- Sandmeyer Reaction
- Wohl-Ziegler bromination
- Balz-Schiemann reaction
- Tsuji-Wilkinson decarbonylation
- Finkelstein reaction
- wurtz reaction
- Barton decarboxylation
- Barton–McCombie deoxygenation
References:
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.
1 thought on “Mechanism Of Hunsdiecker Reaction: carboxylicv acid to Halides”