Table of Page Contents
What is Pinacol Pinacolone rearrangement ?
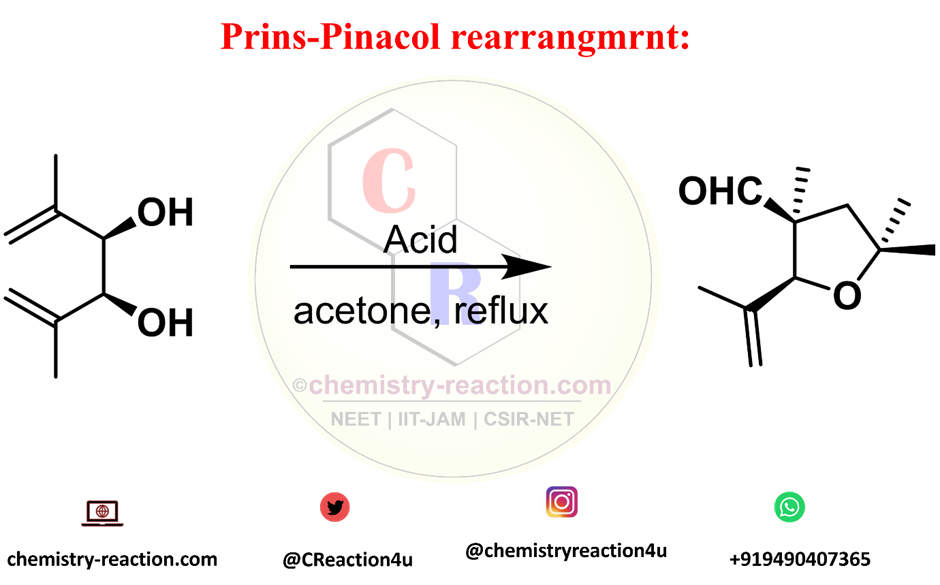
The formation of oxacyclic and carbocyclic ring systems by terminating Prins cyclizations with the pinacol rearrangement in a tandem fashion is known as the Prins-pinacol rearrangement.
it is stereoselective and results in the formation of two C-C bonds, one C-O bond, and two new stereocenters, protic and Lewis’s acids, nitromethane and dichloromethane solvents are the common in used in the reaction. widely used solvents are nitromethane and dichloromethane alkenyl-substituted cyclic acetals derived from 1,2-diols give rise to highly substituted 3-acyltetrahydrofurans
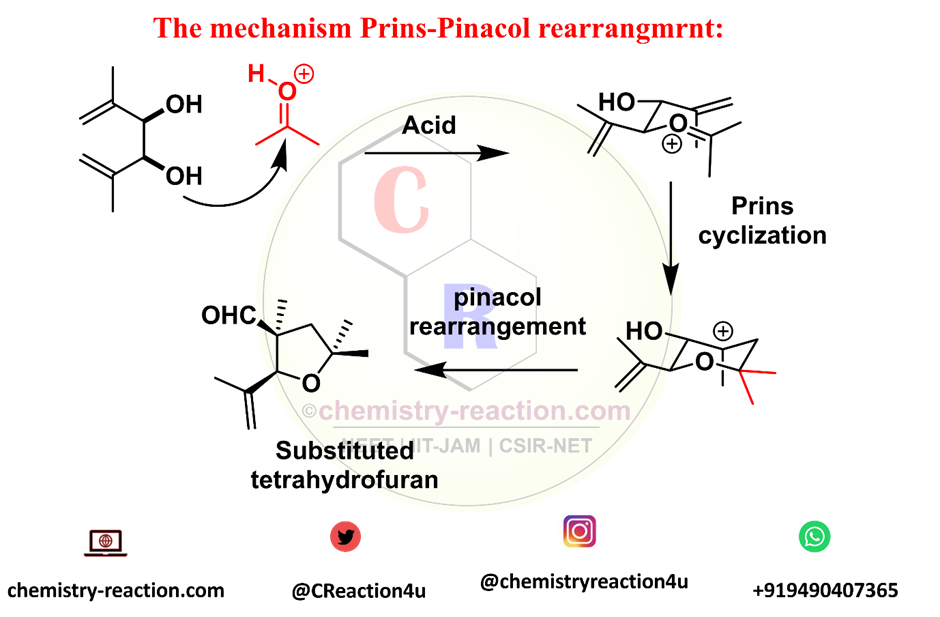
Mechanism Prins-Pinacol Rearrangement :
The reaction was thought to proceed by an oxonia-Cope rearrangement followed by aldol cyclization, but this hypothesis was rejected based on the observation that enantiomerically enriched acetals gave rise to tetrahydrofuran of high enantiomeric purity and not a racemic mixture as was expected.
Related Reactions:
- pinacol rearrangement
References:
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.
1 thought on “Prins-Pinacol Rearrangement :”