Table of Page Contents
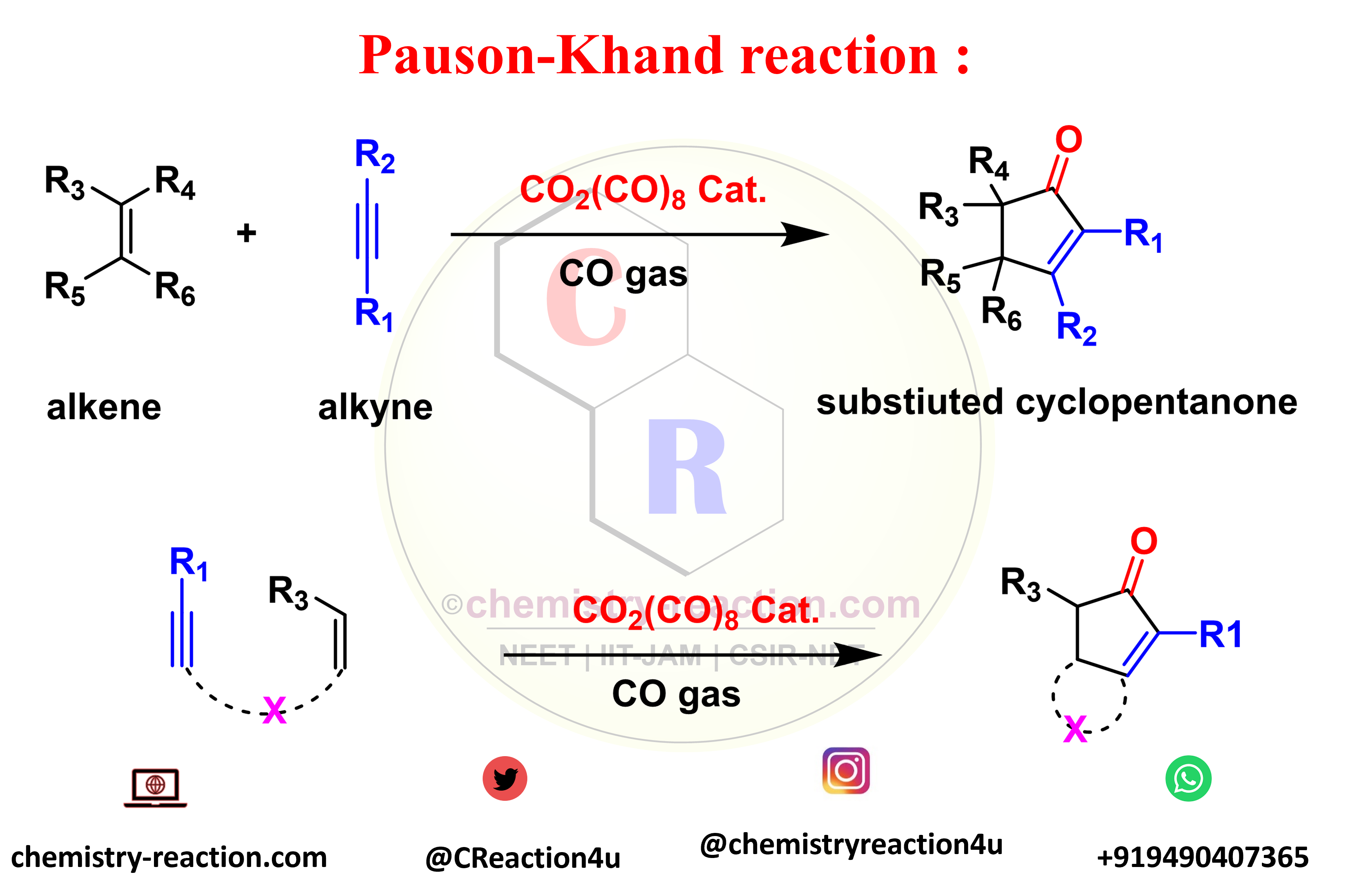
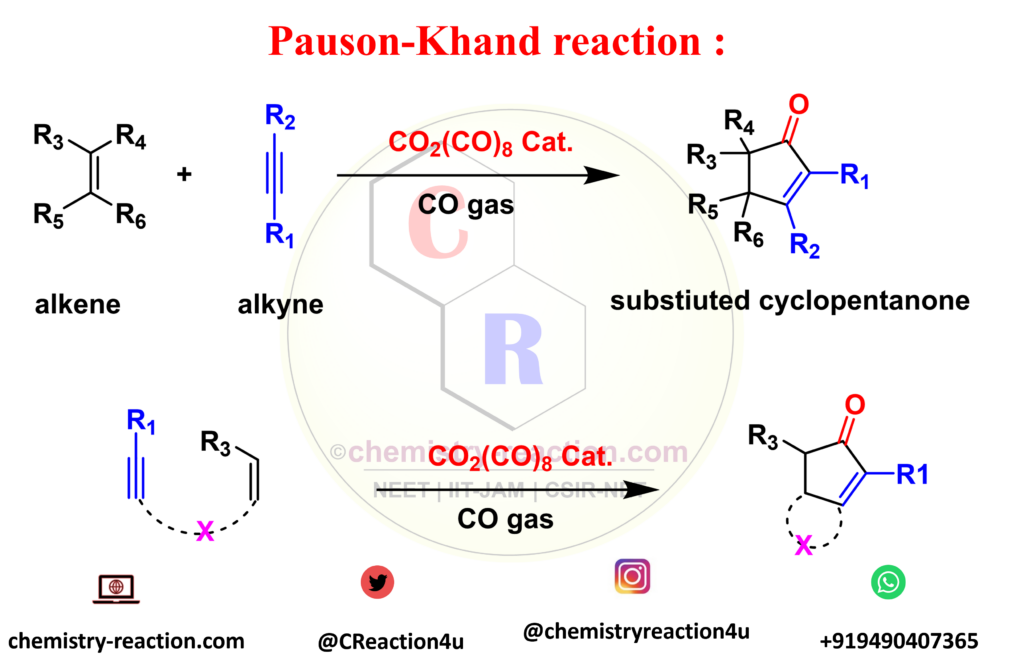
what is pauson-Khand reacction?
The Pauson-Khand reaction is an organic Multiple component reactions organic used to convert an alkyne and alkene to a substituted cyclopentenone by using CO2(CO)8 complex catalyst and an of carbon monoxide. Also known as Pauson-Khand cycloaddition.
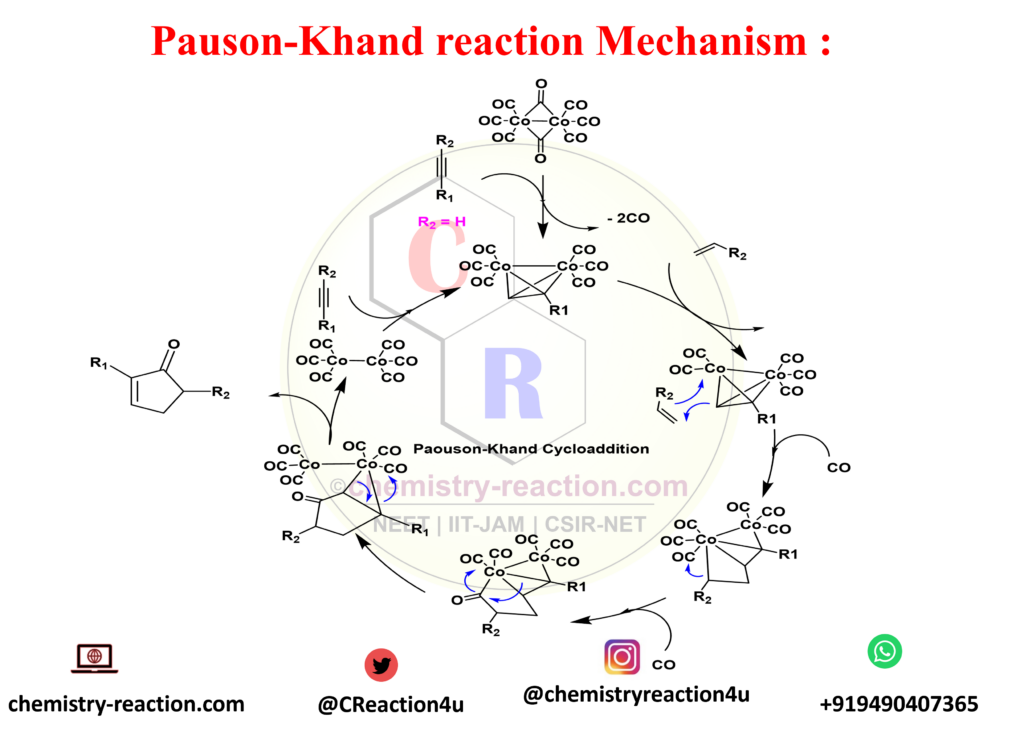
Pauson-Khand Reaction Mechanism :
This is 2+2+1 type of cycloaddition reaction, firstly it start with the addition of the alkyne to the Cobalt complex followed by ligand substitution of the alkene to expel a Carbon monoxide molecule. Alkene insertion follows and a subsequent Carbon monoxide insertion results in the formation of a carbonyl group then reductive eliminations then yield the final cyclopentenone product and regenerates the cobalt catalyst which will further repeat the catalytic process.
Related reactions:
Reference:
- Cabot, R.; Lledó, A.; Revés, M.; Riera, A.; Verdaguer, X. Organometallics 2007, 26, 1134–1142.
- Yamanaka, M.; Nakamura, E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1703–1708.
- Magnus, P.; Principe, L. M. Tetrahedron Letters 1985, 26, 4851–4854.
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.