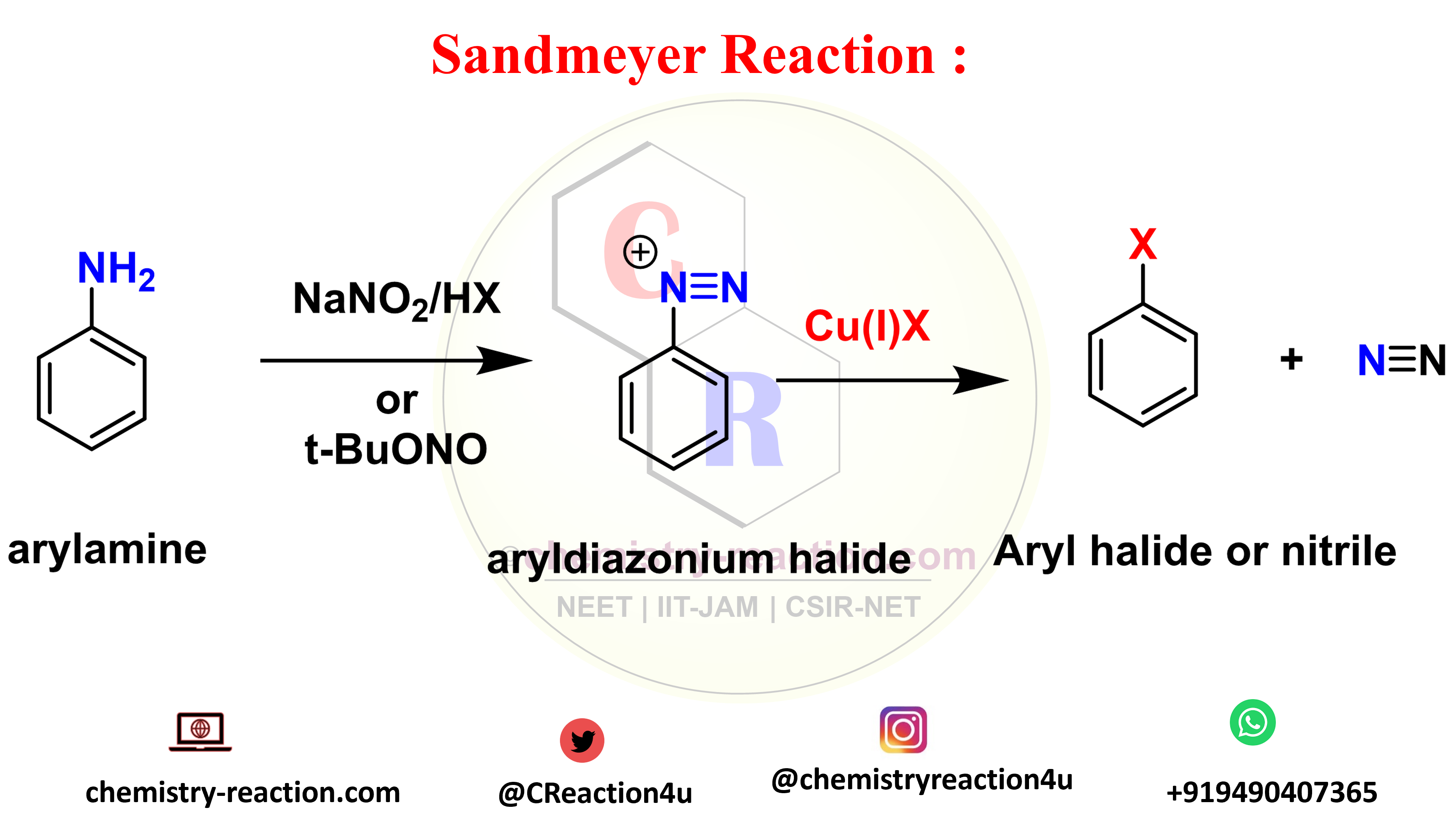
Vilsmeier–Haack formylation
The formylation of electron-rich aromatic compounds with a mixture of dimethylformamide and phosphorus oxychloride POCl3 is commonly referred to as the Vilsmeier reaction, or sometimes the Vilsmeier-Haack reaction, from the names of the two German chemists who first described it in 1927.