Table of Page Contents
What is Pummerer Rearrangement explain?
the Pummerer rearrangement is referred for Formation of α-substituted sulfides from the corresponding sulfoxides (must have at least one hydrogen atom at their α-position).
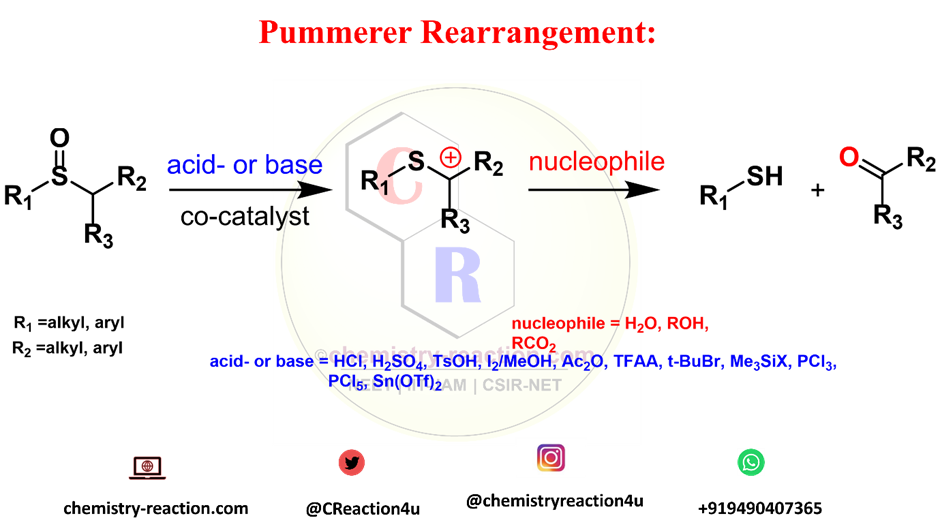
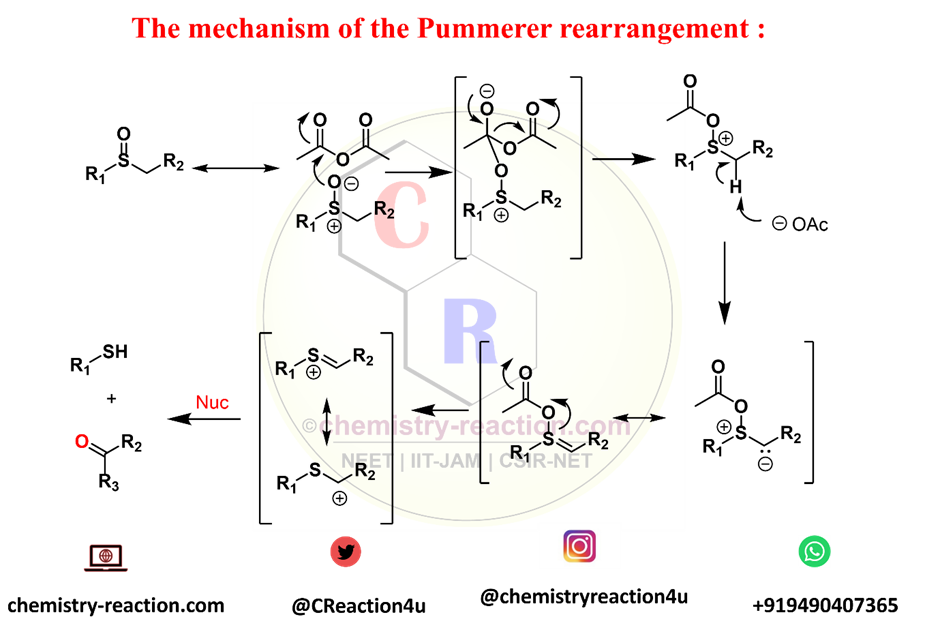
Pummerer Rearrangement Mechanism :
- steps 1: acylation of the sulfoxide oxygen to form an acyloxysulfonium salt
- steps 2 :loss of a proton from the α-carbon to afford an acylsulfonium ylide
- steps 3: cleavage of the sulfur-oxygen bond to give sulfur-substituted carbocation (RDS)
- steps 4: capture of the nucleophile by the carbocation.
Related Reactions:
- Sommelet-Hauser Rearrangement
- Willgerodt Rearrangement
- Payne Rearrangement
- Curtius Rearrangement
- Polonovski Rearrangement
- Smiles Rearrangement
References:
- de Lucchi, Ottorino; Miotti, Umberto; Modena, Giorgio (1991). The Pummerer Reaction of Sulfinyl Compounds. Organic Reactions. Vol. 40. pp. 157–184. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or040.03. ISBN 978-0471264187.
- Padwa, Albert; Gunn, David E., Jr.; Osterhout, Martin H. (1997). “Application of the Pummerer Reaction Toward the Synthesis of Complex Carbocycles and Heterocycles”. Synthesis. 1997 (12): 1353–1377. doi:10.1055/s-1997-1384.
- Smith, Laura H. S.; Coote, Susannah C.; Sneddon, Helen F.; Procter, David J. (2010). “Beyond the Pummerer Reaction: Recent Developments in Thionium Ion Chemistry”. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 49 (34): 5832–44. doi:10.1002/anie.201000517. PMID 20583014.
- Stork Enamine Reaction Mechanism:PPT, PDF, Slideshare (Synthesis)
- Mechanism Of Hunsdiecker Reaction: carboxylicv acid to Halides
- Mannich Reaction : Definition, Mechanism, Application, Explanation
- Stephen Aldehyde Synthesis, Mechanism and Application
- Vilsmeier–Haack formylation
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.
3 thoughts on “Pummerer Rearrangement: Mechanism, Applications Examples”