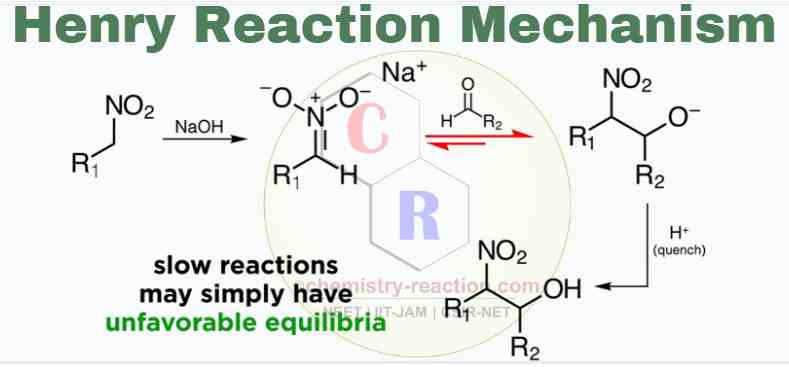
The Henry reaction was first reported by Belgian chemist Louis Henry in 1895. The Henry reaction involves the addition of a nitronate salt to a carbonyl compound, usually an aldehyde. The reaction is also referred to as a Nitroaldol reaction. It is C-C bond-forming reaction used in organic synthesis.
Table of Page Contents
Mechanism:
The Henry Reaction Mechanism can present in two steps
1) Nitronate preparation
Nitronate is usually prepared in situ by treating the nitroalkane with a strong base, like hydroxide, alkoxide, or even an amine base.
2) Addition of Nitronate to aldehyde
Next, an aldol reaction (C-alkylation of the nitroalkane) takes place with the carbonyl compound to form diastereomeric β-nitro alkoxides. Finally the β-nitro alkoxides are protonated to give the expected β-nitro alcohols.
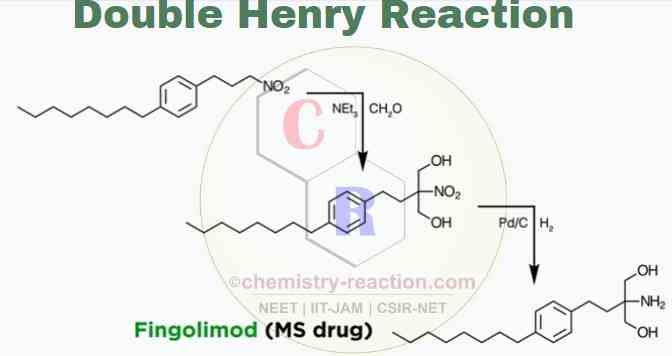
Double Henry Reaction:
In rare cases, the Henry reaction is even too favorable and can occur twice because the product is nitroalkane. This overreaction is encountered almost exclusively with formaldehyde; in these cases, a 2-nitro-1,3-diol is formed, which can sometimes have synthetic value.
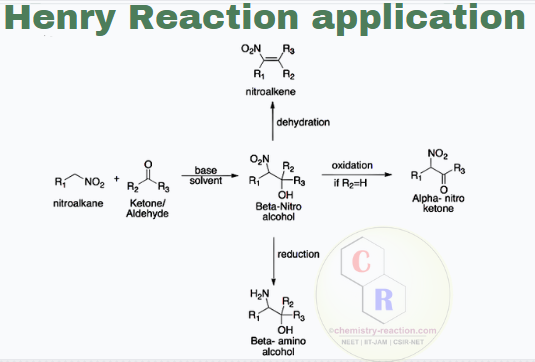
Henry Reaction Examples, Application
- The nitro group is quickly reduced to the amine; therefore, this is a route to 1,2-amino alcohols.
- The Henry product can also be easily dehydrated to a nitro-olefin, which is a Michael acceptor and can be reached at this position with several nucleophiles.
- Especially synthesis of alpha-nitro ketone, is a very versatile tool and is used extensively by organic chemists.
- 1,2-Nitroalcohols are essential intermediates in organic synthesis.
- An example of a tandem Henry plus Nef-reaction is the one-carbon homologation of pentoses to hexoses, meaning that carbon is added from a 5-carbon sugar to a 6-carbon sugar.
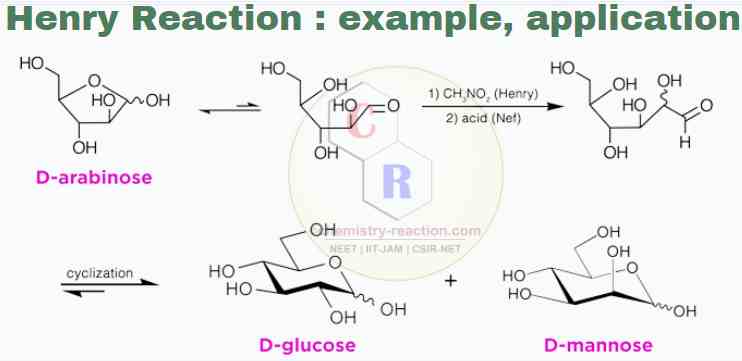
henry reaction pdf, henry reaction dehydration, henry reaction conditions, henry reaction examples
Stereoselective Henry Reaction :
Henry’s reaction has been a prime target for diastereoselective and enantioselective synthesis. BINOL-metal catalysts, best if derivatives of lanthanides, create a chelated, rigid transition state for the reaction and therefore allow for excellent stereocontrol.
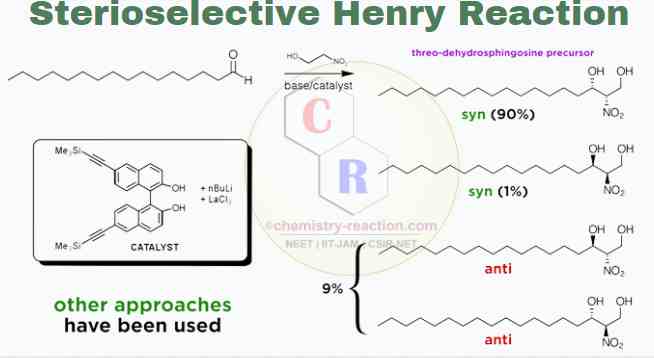
Limitation :
- Henry’s reactions with ketones can be unsatisfactory or even impossible because the equilibrium lies in favor of the nitronate and the ketone.
- Using aldehydes as reactants also brings the danger of base-promoted reactions like aldol condensations and Cannizzaro reactions of the aldehyde. These are the limitation of Henry’s reactions.
Related Reactions :
- Aza-Henry Reaction
- Nef Reaction
References :
- Henry, Louis (1895). Synthetic formation of nitrated alcohols
- ScienceDirect Henry-reaction
- Professor Dave Explains _ Henry reactions
- Henry Reaction review
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.