Smiles rearrangement is an organic reaction known for synthesizing the isomeric compound 2-hydroxy-2′-mercapto-bis-(1-naphthyl) ether, which is the intramolecular nucleophilic aromatic substitution rearrangement.
R. Henriques reported the actual method in 1894. Still, later on, O. Hinsberg carried out similar experiments with the corresponding sulfones, but it was S. Smiles who established the structure of the products.
Electron-withdrawing groups at the ortho- or para positions of the aromatic ring are necessary for activation of the ring for Smiles rearrangement. In case, more than one activating, the groups will help to increase the rate of rearrangement (when R2 =EWG). Instead of substituted benzene rings, the aromatic ring can also be heteroaromatic such as pyridine or pyrimidine.
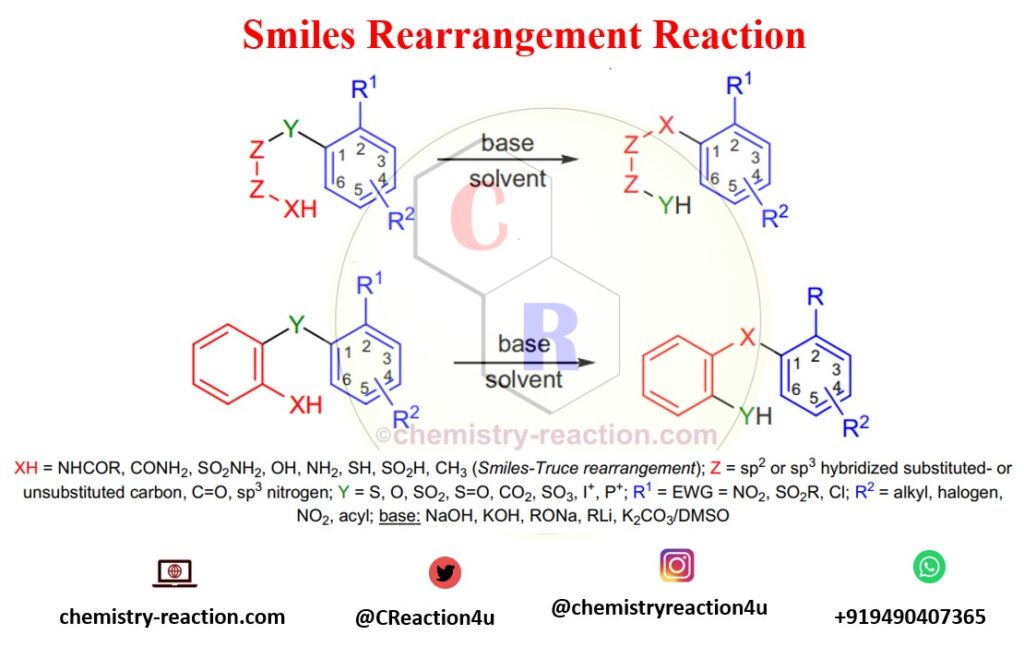
Table of Page Contents
Modifications of Smiles Rearrangement reaction:
- Smiles-Truce rearrangement : refers to when No activating group is required if Y=SO2 and XH=CH3 as substrate and strong base are used in the reaction
- Photochemical Smiles Rearrangement :
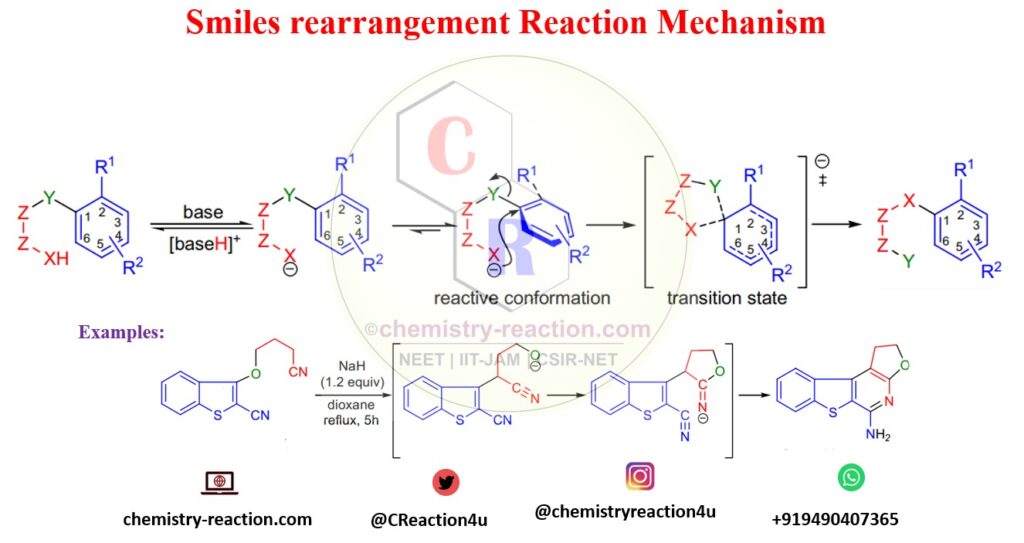
Mechanism of Smiles Rearrangement:
The first step of the reaction mechanism base will deprotonate Y (NHCOR CONH2, SO2NH2, OH, NH2, SH, SO2H, or CH3), and the nucleophile will generate. In the next step, the substrate adopts a reactive conformation in which the plane of the migrating ring is perpendicular to the Z-Z bond. nucleophile attacks the ring in an ipso fashion to form a five-membered transition state that affords the product.
Applications of Smiles Rearrangement:
- The total synthesis of the lichen diphenyl ether epiphorellic acid 1 has been don by using Smiles Rearrangement
- Novel non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, dipyrido[2,3-b]diazepinone
Related Reaction:
- Hofmann Rearrangement
- Curtius Rearrangement
- Beckmann Rearrangement
- Sommelet-Hauser Rearrangement
- Lossen Rearrangement
- Pummerer Rearrangement
References :
- The Smiles and Related Rearrangements of Aromatic Systems”. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/0471264180.or018.02
- The rearrangement of hydroxy-sulphones. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/1931/JR/JR9310003264
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.201507369
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.
2 thoughts on “Smiles Rearrangement Reaction : Mechanism , Application and Modification”