Cannizzaro Reaction is a base-catalyzed redox reaction in which aromatic aldehydes, formaldehyde, or other aliphatic aldehydes lacking α-hydrogen are converted into the corresponding alcohols and carboxylic acids. Cannizzaro reaction is a named reaction in organic chemistry. Here, we will explore the Cannizzaro Reaction and its mechanism, accompanied by some interesting examples.
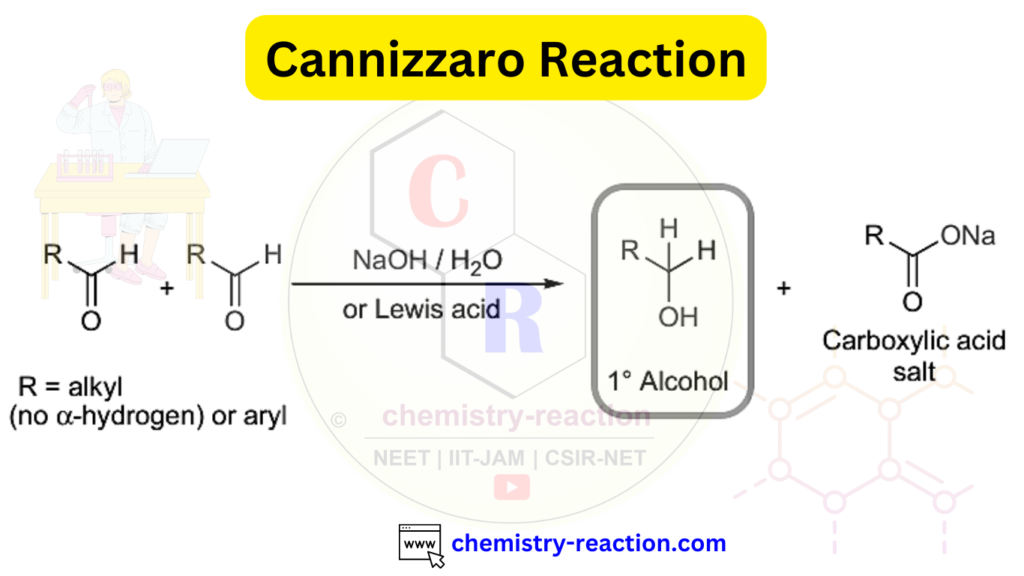
Cannizzaro Reaction Mechanism:
Several mechanisms have been proposed; the hydride transfer mechanism is most widely accepted.
- OH⁻ attacks the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde.
- The adduct is deprotonated under basic conditions to form a dianion.
- The dianion enables hydride (H⁻) transfer from the aldehydic carbon.
- The hydride attacks another aldehyde molecule (rate-determining step), forming an alkoxide.
- The alkoxide is protonated by water to give a primary alcohol.

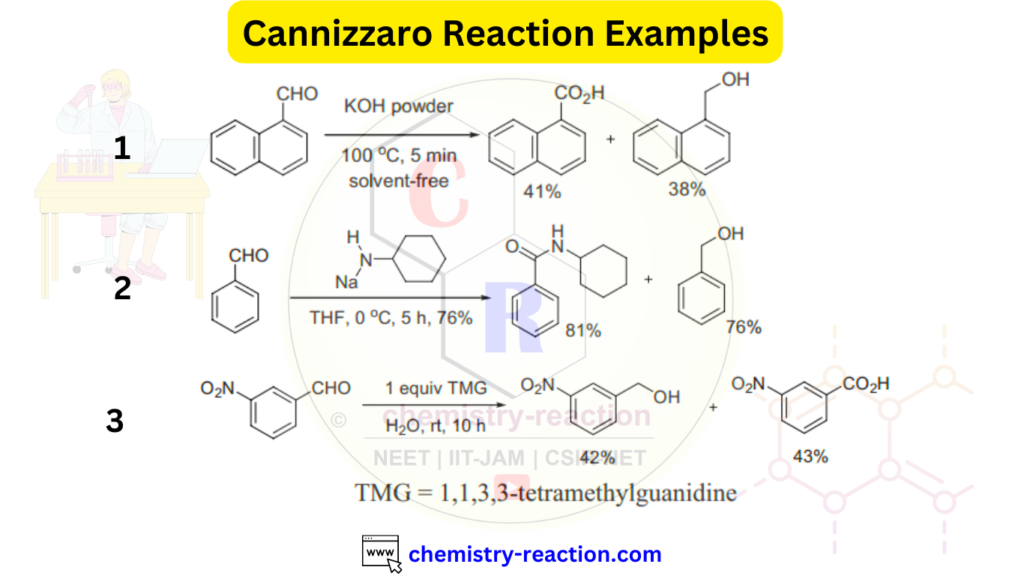
Cannizzaro Reaction Examples:
Here are a few synthetic applications of the Cannizzaro reaction in organic chemistry.
References :
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.