Table of Page Contents
stobbe condensation definition:
Stobbe condensation is a formation of alkylidene succinic acids or their monoesters by the base-mediated condensation of ketones and aldehydes with dialkyl succinates. reagents and mechanism we will discuses in this regard accordingly.
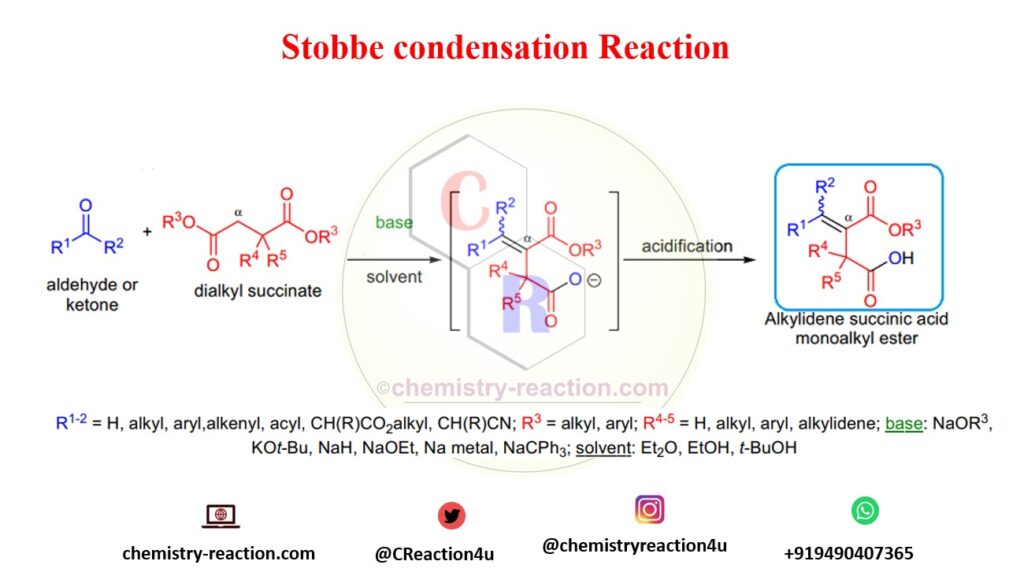
General reagents and condition of the Stobbe Condensation:
- In Stobbe Condensation there is no restriction on the carbonyl component it may have hydrogens at its α-position. aromatic-, α,β-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones as well as aliphatic ones are commonly used;
- the diesters are mainly limited to succinic esters and their substituted derivatives, but certain α,ω-diesters that do not undergo competitive Dieckmann condensation will afford Stobbe products;
- upon mild acidic work-up the primary product is an alkylidene succinic acid monoester;
- when symmetrical ketones are condensed, only one alkene stereoisomer is produced, although unsymmetrical ketones provide a mixture of alkene stereoisomers.
- A variety of products may be formed in Stobbe Condensation, when the carbonyl component has α-protons because of double bond migration under the reaction conditions.
Drawbacks of the Stobbe condensation:
- The aldehyde or ketone substrate will undergoes self-condensation
- Cannizzaro reaction can take place with of aromatic aldehydes
- Highly enolizable ketones give low yields.
- In Stobbe condensation too reactive ketones may undergo acylation (Claisen reaction) at their α-position by the dialkyl succinate.
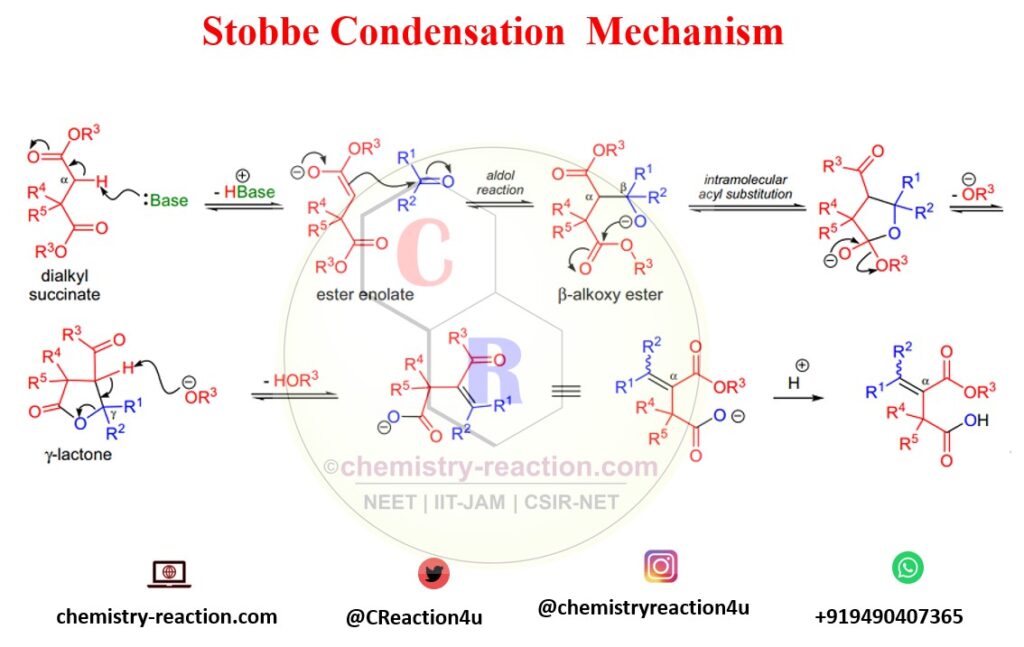
Mechanism of Stobbe Condensation:
The first step of the Stobbe condensation is; the base will deprotonate the succinate at the α-carbon to offer an ester enolate that, in situ, go through an aldol reaction with the carbonyl compound to form a β-alkoxy ester intermediate.
The following intramolecular acyl substitution gives rise to a γ-lactone intermediate which undergoes ring-opening and concomitant double bond development upon deprotonation by the alkoxide ion. Under certain conditions, the lactone intermediate can be separated.
Applications of Stobbe Condensation:
Stobbe Condensation is used to substitute a propionic acid residual for the carbonyl group in aromatic ketones.
When combined with the Friedel-Crafts reaction, this condensation can yield naphthols, indones, and tetralones.
synthesis of γ-keto acids, irreversible ring-opening reactions. synthesis of tree carbon chain
Related Reaction :
- aldol condensation
- benzoin condensation
- Acyloin Condensation
- Claisen Condensation/Claisen Reaction
- Darzens Glycidic Ester Condensation
- Knoevenagel Condensation
References :
- sciencedirect
- https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cber.188101402192
- https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cber.188702001150
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo00897a008
- The Mechanism of the Stobbe Condensation
My name is Pradip Sanjay W. I’m an organic chemist originally from Maharashtra, India. I have qualified UGC NET-JRF, GATE in chemical sciences and MH-SET exam for assistant professor. I’m currently pursuing my Ph.D. in organic chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India.
1 thought on “Stobbe Condensation: Definition, Examples, Reagents and Mechanism”